Find out more about our latest publications

Criteria for Computing Merger Prices of Listed Corporations: Problems and Proposed Improvements
Issue Papers 23-15 Aug. 17, 2023
- Research Topic Capital Markets
- Page 22
Since 1997, Korea's Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act has clearly defined the method for calculating the price of mergers between listed corporations or between listed and unlisted corporations, with the aim of protecting investors and ensuring fair valuation of mergers. However, despite these legislative objectives, the current system for determining merger prices seems to have several side effects, as these prices are primarily determined by market prices.
Based on an analysis of merger cases involving listed corporations in the US and Japan over the past five years, it was observed that merger prices were determined by various methods. This was particularly notable in the cases of small-cap companies, where factors beyond market prices were considered. A close look at Korea's merger cases between listed corporations for the past five years revealed that the cumulative market-adjusted return from one year prior to the merger stood at -6% on average. This suggests possibilities that the selection of when to calculate the merger price was disadvantageous to minor shareholders. The fundamental issue lies in the fact that as long as the merger ratio is determined according to the formula prescribed by law, shareholders have no recourse to address unfair merger ratios.
It is advisable to promote self-regulation in the pricing of mergers, both among affiliated and non-affiliated entities, through indirect regulations that assist the management of merging and merged firms in establishing a fair merger ratio. To be more specific, the board of directors in the merging firm should be granted the authority to determine the price, provided that detailed data regarding the methodology and appropriateness of pricing are disclosed to help shareholders and market participants to make informed decisions about the merger. In cases where a merger could potentially harm the interests of shareholders, additional measures should be implemented to ensure fairness. These measures could include preliminary injunctions against the merger, the appointment of merger inspectors, and imposing liability for damages on those involved.
Based on an analysis of merger cases involving listed corporations in the US and Japan over the past five years, it was observed that merger prices were determined by various methods. This was particularly notable in the cases of small-cap companies, where factors beyond market prices were considered. A close look at Korea's merger cases between listed corporations for the past five years revealed that the cumulative market-adjusted return from one year prior to the merger stood at -6% on average. This suggests possibilities that the selection of when to calculate the merger price was disadvantageous to minor shareholders. The fundamental issue lies in the fact that as long as the merger ratio is determined according to the formula prescribed by law, shareholders have no recourse to address unfair merger ratios.
It is advisable to promote self-regulation in the pricing of mergers, both among affiliated and non-affiliated entities, through indirect regulations that assist the management of merging and merged firms in establishing a fair merger ratio. To be more specific, the board of directors in the merging firm should be granted the authority to determine the price, provided that detailed data regarding the methodology and appropriateness of pricing are disclosed to help shareholders and market participants to make informed decisions about the merger. In cases where a merger could potentially harm the interests of shareholders, additional measures should be implemented to ensure fairness. These measures could include preliminary injunctions against the merger, the appointment of merger inspectors, and imposing liability for damages on those involved.
Ⅰ. 들어가며
기업의 M&A는 기업의 성장·혁신을 촉진하고 경제의 역동성을 제고하는 중요한 수단이고, 최근 글로벌 환경변화에 따라 M&A의 중요성은 더욱 증대되고 있다. 정부에서도 2023년 5월 기업 M&A 지원방안을 발표하면서, 오랫동안 문제로 지적되어 온 합병가액 산정방식에 대한 개선방안을 제시하였다. 합병 공시강화, 외부평가기관 규율 마련을 전제로 비계열사간 합병가액 산정 방법을 자율화하겠다는 방침이다. 다만 계열사간 합병의 경우 비계열사간 합병가액 산정방법 자율화에 따른 시장 영향 등을 보아가며 중장기 검토하겠다고 발표하였다.1)
합병은 회사라는 재화를 거래하는 것으로, 여타 다른 재화의 거래와 같이 매도자와 매수자 간의 협상력과 거래방식에 따라 가격이 달라질 수 있게 마련이다. 이에 미국, 일본, 영국, 독일2) 등 해외 주요국의 경우 합병가액 및 합병비율의 산정을 합병하는 회사들의 자율적 판단에 맡기고 있다. 한편 우리나라에서는 1997년부터 지금까지 상장법인 간 합병 그리고 상장법인과 비상장법인의 합병시 합병가액의 산정 방법에 대해 법에서 구체적으로 정하고 있다. 합병가액 산정방식을 법에서 정하는 독특한 제도는 우리나라의 자본시장이 미성숙했고 상장법인의 수도 적었던 시기에, 시장의 공정성을 확보하고 투자자 보호를 강화하기 위해 금융당국이 직접 합병비율 조정을 권고하는 등 합병 내용의 실질적 심사를 하면서 시작되었다. 이후 주가를 기준으로 합병가액을 산정하는 것에 대한 비판이 계속되면서, 시장주가의 신뢰성 확보를 위한 개정이 여러 차례 있었으나 구체적인 산식의 변화만 있을 뿐 여전히 법에서 합병가액을 정하는 규제는 지금도 유지되고 있다.
그러나 주가에 의해 획일적으로 산정되는 합병가액은 공정한 합병가액의 산정과 투자자 보호라는 당초 법 제정 목적과는 달리 여러 가지 부작용을 낳고 있는 것으로 판단된다. 이에 본 보고서는 합병가액 산정방식을 법에서 정하는 현행 제도를 유지하는 것이 바람직한가에 대한 문제의식을 가지고, 제도의 문제점을 지적한 후 합병가액을 자율화하되 투자자 보호라는 제도의 본래 취지를 달성하기 위한 추가적 개선방안을 제안하고자 한다.
Ⅱ. 합병가액 산정 관련 현행 제도 및 문제점
1. 합병비율 및 합병가액의 중요성
회사는 대내외 경영환경에 대응하여 다양한 조직재편을 시도하는데, 그 중 대표적인 것이 합병이다. 합병은 2개 이상의 회사가 합병계약을 통해, 소멸회사(피합병회사)의 모든 권리 의무를 존속회사(합병회사)가 이전받고 소멸회사의 주주에게 존속회사의 주식 또는 금전 등의 재산을 교부하는 법률행위이다.3) 이 경우 소멸회사의 주주들에게 합병대가로 존속회사의 주식을 몇 주 교부할 것인지가 중요한데, 그 기준이 되는 것이 합병비율이다. 합병비율은 존속회사의 주식과 소멸회사의 주식의 교환비율이고, 결국 소멸회사의 모든 것을 존속회사에 넘기는 대가로 제공되는 ‘가격’이다. 예를 들어, 존속회사와 소멸회사의 합병비율이 1:0.5인 경우 존속회사의 1주와 소멸회사의 0.5주가 같은 가치라는 의미이고 소멸회사의 주식을 1주 가지고 있는 주주는 존속회사의 주식 0.5주를 받을 수 있게 된다. 합병비율에 따라 주주들이 받게 되는 주식의 수가 달라지므로, 합병비율은 주주들의 이해관계에 직접적인 영향을 미치게 된다.
그런데 합병비율은 합병계약을 체결하는 회사들의 이사회에서 결정되고, 주주는 이미 결정된 합병비율에 대하여 주주총회에서 찬성 혹은 반대의견을 낼 수 있을 뿐, 합병비율 결정에 직접적으로 관여하지는 못한다.4) 따라서 이사회와 주주 간, 혹은 주주들 간의 이해관계가 다를 경우 일부 주주에게 불리한 합병비율로 합병이 진행될 가능성이 있다. 이러한 문제점을 보완하고 주주의 이익을 보호하기 위하여, 우리 법제는 공정한 합병비율을 보장하기 위한 합병가액 산정에 관한 규정을 마련하고 있다. 합병가액은 합병비율을 산정하는 근거로, 존속회사와 소멸회사의 합병가액의 비율이 합병비율이 된다. 예를 들어, 존속회사의 합병가액이 2만원, 소멸회사의 합병가액이 1만원인 경우, 합병비율은 2만원:1만원, 즉 1:0.5가 된다. 자본시장법은 상장법인의 경우 주가를 기준으로, 상장법인과 합병하는 비상장법인의 경우 자산가치와 수익가치를 기준으로 합병가액을 산정하도록 규정하고 있다.
2. 현행법상 상장법인의 합병가액 산정방법
가. 상장법인에 대한 합병 관련 규제의 입법취지와 연혁
1962년 증권거래법(법률 제972호, 1962. 1. 15, 제정)이 처음 제정되었을 당시에는 상장법인의 합병과 관련하여 특별한 규제가 없었으나, 1976년 증권거래법(법률 제2920호, 1976. 12. 22, 전부개정)을 전면적으로 개정하면서 상장법인이 비상장법인과 합병하는 경우, 비상장법인에 대하여 합병승인을 위한 주주총회일 6월 전에 증권관리위원회에 등록하도록 하였다(제3조). 더불어 합병계약승인결의시 상장법인에 대하여 이를 증권관리위원회와 거래소에 신고하도록 하였다(제186조 제7항).
그러나 합병사실을 신고하는 것만으로는 합병의 공정성이나 타당성을 판단하는데 필요한 정보를 투자자들에게 충분히 제공할 수 없다는 문제가 제기되었고, 이에 1991년 증권거래법(법률 제4469호, 1991. 12. 31, 일부개정)을 개정하여 합병신고제도를 도입하였다(제190조의2). 합병신고제도의 도입 이후 증권관리위원회에서는 합병신고서를 검토하면서 합병의 보류, 합병비율 조정의 권고 등 상장법인 합병의 실질적 내용에 관한 규제를 하였고, 1997년 증권거래법(법률 제5254호, 1997. 1. 13, 일부개정) 개정을 통해 합병가액 등 합병 요건 및 절차에 대한 규제를 도입하였다. 도입 당시에는 주권상장법인(유가증권시장 상장법인)에 대해서만 규제하였으나 이후 협회등록법인(코스닥시장 상장법인)에도 적용하여 규제 범위는 확대된 반면, 합병가액을 산정하는 구체적인 산식의 변화만 있을 뿐 법에서 합병가액을 정하는 규제는 지금도 유지되고 있다.5)
나. 상장법인 합병가액 산정기준의 변화
주가를 기준으로 합병가액을 산정하는 것에 대한 비판이 계속되면서, 시장주가의 신뢰성 확보를 위한 개정이 여러 차례 있었다. 합병신고서 제출 전일을 기준으로 주가를 산정하던 기준을 이사회 결의일 또는 합병계약 체결일 중 앞서는 날의 전일로 하여 합병이 주가에 미치는 영향을 최소화하고자 하였다. 또한 제도의 도입당시에는 1개월간의 최종시세가격만을 기준으로 산정하였으나 이후 최근 1개월간의 종가 및 거래량을 이용하여 가중 평균한 값을 기준으로 기준시가를 산출하고6), 할인 또는 할증할 수 있도록 하는 재량권도 허용하였다.

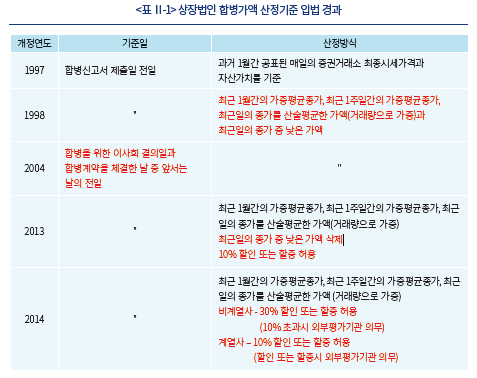
다. 상장법인 합병가액 산정방식의 의무화
현행법상 상장법인의 합병가액은 합병에 대한 이사회 결의일 또는 계약체결일 중 빠른 날의 전일을 기산일로 하여 과거 1개월, 1주일, 직전일의 종가를 거래량으로 각각 가중평균한 후 산술평균한 값을 기준시가로 하여, 비계열사간 30%, 계열사간 10%의 범위에서 할인 또는 할증할 수 있도록 정하고 있다. 다만 비계열사가 10%를 초과하여 할인 또는 할증하거나 계열사가 기준시가를 초과하여 할인 또는 할증하는 경우 외부평가기관의 평가를 의무적으로 받아야 한다. 상장법인과 비상장법인의 합병시 상장법인은 기준시가를 기준으로 하되 기준시가가 자산가치에 미달할 경우 자산가치를 적용할 수 있도록 하고, 비상장법인은 자산가치와 수익가치를 각각 1과 1.5로 가중평균하여 산정한 본질가치를 합병가액으로 하도록 한다(자본시장법 시행령 제176조의5).
이러한 합병기준이 실무에서는 사실상 강제되는데, 이를 준수하지 않으면 금융감독원에서 존속회사가 제출하는 증권신고서를 자본시장법 제120조 제2항에 근거하여 수리하지 않기 때문이다.7) 법에서 획일적인 산정기준을 정해줌으로써 합병가액 산정의 신속성과 비용부담 절감 등에 기여하였고8), 신뢰할 수 있는 거래소 주가를 통해 평가자의 의문을 최소화하고 예측가능성을 제고하였다는 긍정적 평가도 있다.9) 그러나 합병거래의 조건을 당사자의 자율적 교섭에 의하지 않고 법에서 정하도록 함으로써 당초 입법취지와 달리 투자자들에게 부정적인 영향을 끼치고 있다는 문제도 지적되고 있어 아래에서는 이 부분을 자세히 살펴보고자 한다.
3. 상장법인 합병가액 산정방식의 문제점
가. 시장주가에 의존한 획일적 산정방식
이론상 가격은 시장에서 평가된 기업의 가치를 반영한다는 점에서 합병가액 산정의 타당한 근거가 될 수 있다. 그러나 가격은 기업의 내재가치 이외의 다른 요인들에 의해서 매일 변동하게 마련이다. 회사가 합병을 결정할 때는 회사의 시장주가도 중요한 기준이 될 수 있지만 합병으로 인한 당사 회사의 상호보완성 및 시너지 효과, 회사의 연구개발인력의 자질, 경영진의 자질 같은 무형의 자산들도 중요하게 여겨질 수 있다.10) 이러한 이유로 자본시장이 발달한 미국, 영국, 일본 등 주요국에서도 합병가액 및 합병비율의 산정을 합병하는 회사의 자율적 판단에 맡긴다.
초기 미국의 판례를 보면 시장가치법에 의하여 주식가격을 결정하는 입장이었는데 시장가치의 신뢰성에 대한 문제가 제기되면서, 1980년 델라웨어주는 Bell v. Kirby Lumber Co. 판결에서 시장가치, 자산가치, 수익가치를 가중평균하는 방법으로 주식의 가치를 산정하였다. 이는 델라웨어 가중평균법으로 불리우며, 이후 다른 주 법원의 판결에 영향을 미쳤다. 델라웨어주 대법원은 1983년 이른바 Weinberger v. UOP. 판결에서, 그동안 사용했던 델라웨어 가중평균법을 탈피하고 새로운 주식가격산정방법으로 현금흐름할인법(DCF)을 제시하였다. 이후 현금흐름할인법이 많이 활용되었으나, 2017년 DFC Global Corp. v. Muirfield Value Partners, L.P 판결에서는 거래가격이 가장 믿을 수 있는 가치라고 판단하기도 하였다. 일본의 경우 합병비율은 존속회사와 소멸회사의 경영진이 합의한 주식 및 기업가치 평가액에 근거하여 산정하는데, 일본의 최근 5년간 합병공시를 검토한 결과, 시장주가법과 현금흐름할인법이 가장 많이 쓰였고 그 외에 유사기업 비교법 정도를 사용하고 있다.
법에서 합병가액 산정방식을 정한 주요 목적은 투자자 보호이다. 법원은 자본시장법 시행령에서 정한 합병가액의 입법취지를 “주권상장법인의 경우 수많은 투자자들이 관련되어 있어서 합병가액을 규제함으로써 투자자를 보호할 필요성이 높기 때문”이라고 해석한다.11) 현행법에 따른 합병가액 산정이 획일적이라 하더라도 투자자 보호라는 당초 입법취지를 달성하고 있다면 큰 문제가 되지 않을 것이다. 그러나 미국과 일본의 합병에서 실제로 거래된 합병가액과 국내의 기준시가 산정방식으로 도출한 합병가액을 비교한 결과, 국내의 합병가액 산정방식이 당초 입법취지와는 다르게 작용하고 있는 것으로 보인다.
2019년 1월부터 2023년 4월까지 미국의 상장법인간 합병 총 333건에 대하여 우리나라 자본시장법에 따라 소멸회사의 기준시가를 산출해 실제 거래된 합병액12)과 비교하였다.13) 아래 <표 Ⅱ-2>를 보면 실제 발표된 미국 상장회사의 합병가액이 우리나라 자본시장법에 따른 기준시가 이상인 경우가 전체의 86.2%(287건)에 달했다. 기준시가를 10% 할증한 가격 이상으로 거래된 경우는 77.2%(257건), 기준시가를 30% 할증한 가격 이상 거래된 경우도 56.8%(189건)으로 우리나라 자본시장법상 합병가액으로 허용될 수 있는 가격보다 훨씬 더 높은 가격으로 합병이 성사되는 것으로 나타났다.
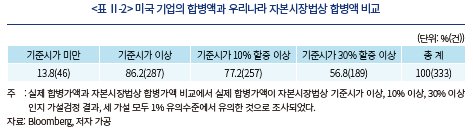
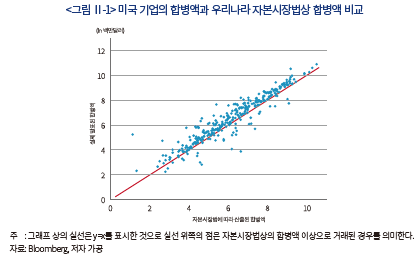
아래 <그림Ⅱ-1>은 조사 대상 기업들의 실제 거래액과 우리나라 자본시장법에 따라 산출한 합병액을 비교한 것이다. 아래 그림을 보면 자본시장법에 따른 합병액이 유사한 기업들간에도 실제 발표된 합병액에는 차이가 존재하는 것을 볼 수 있다. 기업의 시가총액 규모가 유사해 주가에 근거한 합병액은 유사하게 산출된다 하더라도, 기업간의 이질성으로 인해 합병에서 평가되는 소멸회사의 가격은 달라질 수 있는 것이다.
또한 시가총액이 높은 기업일수록 실제 거래액과 합병액의 괴리가 상대적으로 적은 것으로 나타났다. 규모가 작은 기업의 경우, 시장에서 공유되지 않은 기업의 내재가치 정보, 기업의 잠재력, 성장가능성 등이 합병가액의 결정요소로 작용해, 주가를 이용해 산출하는 자본시장법상의 합병가액과 실제 거래액의 차이가 크게 나타났을 수 있다. 반면 시가총액이 높은 기업은 시장에서 기업의 가치가 충분히 판단되었고, 가격에 반영되지 않은 내재가치가 적어 자본시장법상의 합병가액과 실제 합병가액의 괴리가 상대적으로 적게 나타난 것이라고 해석할 수 있다.14)
다음으로 일본의 실제 합병액을 살펴보기 위하여 앞서 기술한 방식으로 2019년 1월부터 2023년 4월까지 88건의 합병 데이터를 분석하였다.15) 아래 <표 Ⅱ-3>을 보면 분석에 사용된 88건 중 발표된 합병액이 자본시장법에 따라 산출한 기준시가 이상인 경우는 전체의 90.9%(80건)에 해당했다. 기준시가의 10% 이상의 가격으로 거래된 경우가 전체의 81.8%(72건), 30% 이상인 경우도 55.7%(49건)로 매우 높게 나타났다. 미국의 경우와 마찬가지로, 일본에서도 국내 합병액보다 높은 가격에 합병이 진행되는 것을 알 수 있었다.
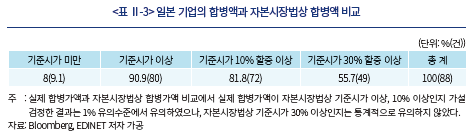
미국과 마찬가지로 일본의 합병 기업들의 실제 합병액과 우리나라 자본시장법에 따라 산출한 합병액 비교를 아래 <그림 Ⅱ-2>에 나타내었다. 일본의 합병액은 미국의 경우보다 그 분포가 작지만, 여전히 다양하게 분포하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 또한 미국과 마찬가지로, 시가총액이 낮은 기업의 경우 한국식으로 산출한 합병액과 실제 거래액의 괴리가 큰 반면, 시가총액이 높은 기업들의 경우에는 비교적 한국식 합병액과 비슷한 가격에 거래가 되는 것으로 나타났다.16)

미국과 일본의 합병사례만 분석해 보아도, 기업별로 다양하게 합병가액 산정이 이루어지고 있고 특히 시가총액이 낮은 기업의 경우 시장주가 외에도 다양한 요소가 고려되고 있음을 알 수 있다. 한편 시장주가만을 기준으로 하여 획일적으로 합병가액을 산정하는 우리나라 자본시장법의 규제로 인해 주주들의 주식가치가 적절하게 평가받지 못할 가능성이 있다. 물론 주식매수청구권을 행사하여 보호받을 수 있다고 생각할 수 있으나, 자본시장법에서 주식매수청구권의 계산방식도 시장주가를 기준으로 하고 있어 동일한 문제가 발생한다. 특히 합병에서 정당한 가치보장이 이루어지기 위해서는 소멸회사의 주주에게 청산가치 이상을 보장해야 하는데, 시장주가가 순자산가치에 현저히 미달하는 경우에도 자본시장법 시행령에 의해 산정되었다는 이유로 공정하다고 판단하는 것은 타당하지 않다.17)
합병가액 산정방식을 법에서 정하고 있다 보니 합병 관련 기관들의 도덕적 해이도 발생한다. 합병가액 산정에 있어 주주의 이익에 부합하도록 최선을 다해야 하는 이사회도 회사의 진정한 경제적 가치를 측정하고 더 나은 합병 조건을 협상하기 위한 노력을 기울일 필요가 없게 된다. 또한 타인의 자산을 수탁받아 운용하는 연금이나 투자펀드 등의 기관투자자에게도 현행의 제도는 투자 대상인 합병 기업의 경제적 가치를 평가하여 적절한 조치를 취할 의무를 사실상 면제하고 있다. 합병가액에 대해 평가하는 회계법인 역시 법에서 정한 산식을 준수하였는지 여부만 판단하면 되는 것이 현실이다. 이러한 점을 종합할 때 시장주가에 의존한 획일적 산정방식은 투자자 보호라는 당초 입법취지를 달성하지 못하고 있는 것으로 판단된다.
나. 합병시점의 임의성
시장주가를 해당 기업의 객관적 가치가 반영된 가격으로 신뢰할 수 있는 경우에도, 합병시점의 선택에 있어서는 소수주주보다 지배주주의 의견이 더 크게 반영될 수 있다는 문제가 제기될 수 있다. 2018년부터 2022년 12월말까지 발표된 모든 상장사간 합병(16건)을 살펴본 결과, 합병가액은 모두 자본시장법에 따른 기준시가로 결정되었다.18) 해당 기간 존속회사와 소멸회사의 주가수익률을 보면, 합병 발표 1년 전부터 누적 시장조정수익률은 –16.0%로 나타났다. 이는 합병시점이 소수주주에게 불리하게 선택되었을 가능성이 있음을 시사한다.19) 대법원에서도 2015년 삼성물산과 제일모직 합병 승인 이사회 직전 삼성물산 주가는 회사의 적정가치를 표시하지 못한다고 판단하면서, 주식매수가격의 기준시점을 합병일이 아닌 제일모직의 상장 전일로 하여 주가를 산정하도록 결정하였다(대법원 2022. 4. 14. 자 2016마5394 결정).
이러한 실제 사례들을 보면서 투자자들은 일정 시점의 주가를 신뢰하기 어렵게 되고, 합병가액의 공정성에 대한 문제를 제기하게 된다. 지배주주가 시세조종 등 별다른 위법행위를 하지 않더라도, ‘합병의 시점’을 선택할 수 있다 보니 소수주주에게 불리한 시기에 합병할 수 있는 가능성이 있다. 더욱이 현재 우리나라 상장법인 간 합병은 모두 계열사간 합병인데, 의도적으로 일방 계열회사의 주가를 띄우거나 억누를 가능성이 있으므로, 시가는 정확한 잣대가 되지 아니한다는 비판도 있다.20)
그러나 합병비율이 불공정해도 법에서 정한 산식대로 했다면 주주들은 합병 무효의 소송을 제기하기 어렵고 실질적으로 구제를 받을 수도 없다. 합병의 무효는 실제 사건화된 경우가 매우 적어 합병무효에 관한 대법원 판결은 3건21)에 불과하고22), 법에서 정한 합병가액 산정방식을 따른 이상 합병비율의 현저한 불공정으로 인한 합병무효는 인정되지 않았다. 법에서 합병가액의 산식을 규정하고 있기 때문에 법원은 합병비율이 공정한지에 대해 면밀히 판단하지 않으며, 불공정의 입증책임도 오로지 원고의 부담으로 작용한다.23) 그런데 소수주주 입장에서는 회사 내부의 사정에 대해 정확히 알지 못하고, 회사가 진행 중인 사업에 대한 정보가 제한적이므로 지배주주 또는 경영진 주도하에 은밀하게 이루어지는 주가에 대한 영향력 행사(특히, 의도적인 경영부진으로 인한 주가하락)를 입증하기가 쉽지 않다.24) 결과적으로 법에서 정한 합병비율이 합병의 불공정으로부터 주주들을 보호해 줄 수 없게 만들 뿐 아니라, 합병 시점이 적절한가에 대한 투자자들의 불신을 초래하는 문제가 있다.
다. 합병가액의 불확실성
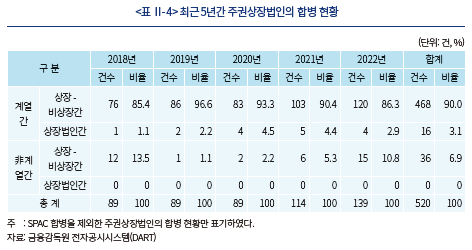
우리나라의 경우 상장법인간 합병은 거의 이루어지지 않는데, 최근 5년간 주권상장법인의 합병 총 520건 중, 상장법인간 합병은 16건으로 전체 3.1%에 불과하다. 또한 이 16건은 모두 계열사간 합병으로, 독립적인 당사자에 의한 합병인 비계열사간 합병은 전무하다. 최순영·김종민(2018)에서도, 1999년에서 2016년 사이 금융회사를 제외한 상장사 간의 합병 106건 중 존속회사와 소멸회사가 서로 독립적인 경우는 10건(9.4%)으로 조사한 바 있다.
상장법인간 합병에 영향을 미치는 요인은 여러 가지가 있겠으나, 실무적으로 보면 현행법상 합병비율의 산정방식 역시 영향을 준 것으로 보인다. 합병비율은 합병회사의 내재적 가치뿐 아니라 각 회사가 처한 사업환경, 교섭력 등을 종합적으로 반영한 줄다리기 협상 끝에 결정되므로 개별 사안마다 다를 수 있다.25) 그런데 우리나라의 경우 법에서 합병가액 산정방식을 정하고 있어, 합병하는 회사들의 자율적 교섭으로 합병가액을 대략적으로 정했다 하더라도, 최종 합병가액은 법에 의해 이사회결의 전일에 정해지게 된다. 이사회 결의일 또는 계약체결일 중 빠른 날의 전일을 기산일로 하여 직전일까지의 종가를 거래량으로 가중산술평균하여야 하므로 이사회 결의일 직전에 합병비율과 그에 따른 합병가액이 확정된다. 만약 사전에 협의한 합병가액과 실제 확정된 합병가액이 괴리가 클 경우 합병이 성사되기 어렵고, 결국 회사는 합병계약을 해제하고 적절한 시점을 기다려 다시 합병을 추진해야 하는데, 이는 실무상 비현실적이다.26) 합병계약에 이르기까지 기업실사 등 복잡한 절차를 거치며 시간과 노력을 투입하게 되는데, 결국 합병 여부가 법에서 정한 방식에 따라 이사회 결의일 전 주가에 의해 좌우될 수 있다는 불확실성으로 인해 회사는 합병을 주저하게 된다. 지배구조나 사업구조 재편 같은 요소가 중요하게 여겨질 수 있는 계열사간 합병은 상대적으로 합병비율의 영향을 덜 받을 수 있으나, 특히 기업가치만을 기준으로 거래를 하는 비계열사간 합병은 합병비율과 그에 따른 합병가액의 불확실성으로 인한 리스크의 영향을 더 받게 마련이다.
회사의 구체적 상황에 따라 회사의 가치평가 방법은 다양할 수 있는데, 법에서 정한 획일적 기준을 적용하므로 당사자 사이의 협상 여지를 차단하게 되고 심한 경우 거래를 가로막을 수도 있다. 뿐만 아니라 이사회 결의일 전일의 시장 주가에 따라 합병가액이 달라지는 불확실성으로 인해 회사는 합병을 주저할 수 있다. 결과적으로 회사 입장에서 보면 현행법상 합병가액 산정기준으로 인해 합병을 선호하지 않게 되고, 회사의 자유로운 M&A 거래를 저해하는 문제가 발생하게 된다. 회사가 M&A를 통해 새로운 사업에 진출하고 규모의 경제를 이루어 기업가치를 극대화하는 것은 투자자에게도 긍정적으로 작용할 수 있는 것으로, 이러한 기회가 제한되는 것은 투자자에게 부정적 영향을 미치는 것이라 볼 수 있다.
Ⅲ. 합병가액 산정 관련 제도 개선 방안
1. 합병가액 산정방식의 완전 자율화
회사가 자율적으로 다양한 가치를 고려하여 합병비율을 산정하되, 그렇게 산정한 이유와 그 비율의 공정성을 회사가 입증하도록 하여 시장의 평가를 받게 제도를 설계하는 것이 필요하다. 해외 주요국의 입법례에 비추어 볼 때도 합병가액 산정방식을 직접 법에서 규제하는 것보다 합병하는 회사의 경영진이 공정한 합병비율을 도출할 수 있도록 간접적인 규제방식을 채택하는 것이 바람직하다. 합병하는 회사의 이사회가 회사의 이익에 부합하도록 최선을 다해 협상하여 합병비율을 선정하고, 산정방식과 합병가액의 적정성에 대한 이사회의 의견 등 합병 관련 주요 정보를 시장에 투명하게 공시하도록 하는 것이 필요하다. 이러한 공시를 검토한 결과 주주의 이익을 해할 수 있는 합병으로 판단될 경우 주주들이 합병에 대한 문제를 제기할 수 있도록 절차적으로 보호하는 제도의 보완이 필요하고, 계열사간의 합병에서는 그러한 공정성을 위한 절차를 더욱 강화해야 한다.27)
금융당국이 발표한 제도개선방안에 따르면 비계열사간 합병만 자율화하고 계열사간 합병은 현행 제도를 유지하는 것으로 하고 있으나, 앞서 언급한 문제점에 비추어 볼 때 계열사간 합병 역시 자율화하되 공정성을 담보하기 위한 다른 방안으로 보완하는 것이 적절하다. 계열사간 합병에 대주주의 영향력에 대한 우려가 있다 하여도 합병가액의 평가를 시가에 의존하는 것이 오히려 시가의 왜곡을 불러올 수 있는 한계도 존재하고28), 합병가액의 산정방식을 자율화하고 그 타당성을 회사가 입증하게 한다면 시장에서 이에 대한 판단을 할 수 있게 마련이다. 만약 합병비율이 일반주주에게 불리하게 제안될 경우, 기관투자자가 적극적으로 반대 의사를 표시하고 다수의 소수주주가 주식매수청구권을 행사할 경우 합병비율의 조정이 이루어질 수 있게 된다. 이러한 점에 비추어 볼 때 계열사간 합병을 자율화 한다고 하여 일반 주주에 불리한 합병비율이 제시될 것이라고 사전에 예단할 수 없을 것이다.
2. 합병가액 산정방식에 대한 공시 강화
합병하는 회사의 이사회에서 합병가액을 자유롭게 산정하고, 그 산정방식과 가격의 적정성에 대한 구체적 정보를 공시하도록 하여, 주주들과 시장 참여자들이 합병에 대해 판단할 수 있도록 하여야 한다.29) 현재도 회사가 합병계약을 체결하면 이사회 또는 합병계약서 체결 후 3일 이내에 주요사항보고서를 제출하여 공시하도록 하고 있다. 이 때 이사회의사록, 합병계약서, 외부평가의견서 등의 서류를 첨부하여야 하고, 기업공시서식에 의해 합병의 목적, 합병의 중요 영향 및 효과, 합병비율, 합병비율의 산출근거가 공시되고는 있다. 그러나 현재 공시되는 내용만으로는 투자자 입장에서 합병비율의 적정성과 합병의 타당성 등을 검토하기에 충분하지 않다.
미국의 경우 SEC는 합병과 관련하여 다양한 보고서를 요구하는데30), 특히 주주총회 이전에 주주들의 합병 찬반의 의사결정을 돕기 위해 제공되는 보고서인 DEFM 14A 양식에는 합병과 관련하여 상세한 정보를 제공하도록 하고 있다. 구체적으로 합병의 배경, 경과와 합병가액 적정성을 포함한 합병의 긍정적·부정적 요인 관련 이사회 의견, 합병에 대한 임원의 이해관계, 합병 자금 조달, 외부 전문가의 의견 등이 포함되어 있다. 합병 관련 또 다른 공시서식인 S-4에서는 거래 조건, 위험 요소, 비율, 추정 재무 정보 및 인수 대상 회사와의 중요한 계약에 관한 정보를 포함할 것을 요구한다. 영국의 경우 합병의 효과, 중요한 이해관계에 미치는 영향, 합병의 내용, 합병비율의 법률적/경제적 측면의 검토내용과 결과 등이 포함된 이사회 설명보고서를 작성하여야 하고(회사법 제908조), 독립된 외부 전문가의 의견31)도 함께 공시하여야 한다(회사법 제909조). 독일 역시 합병보고서에 합병목적, 합병비율과 합병교부금, 합병계약서에 대한 법적·경제적 설명과 근거를 요구하며 특히 합병하는 회사의 기업가치 평가 시 특별한 어려움과 합병이 주주의 지분관계에 미치는 영향에 대한 설명이 담기도록 하고 있다(조직재편법 제8조). 일본의 경우 법에서 합병대가의 산정방법과 그 상당성에 관한 사항뿐 아니라 계열회사간 합병의 경우 소멸회사의 주주의 이익을 해치지 않도록 유의한 조치에 대한 내용32)을 기재하도록 하고 있다(회사법 제782조). 더불어 금융상품거래법에 따른 주요사항신고서와 유가증권신고서에 합병비율, 산정방법, 외부기관자문여부 및 그 내용을 기재하는데 특히 존속회사/소멸회사별로 타당성 확보 및 이해상충방지를 위한 조치내용을 포함하여 기재하도록 하고 있다.
이러한 해외 입법례를 참고하여 상법 또는 자본시장법의 상장법인 특례규정을 개정하거나 공시서식을 개정하여 더 많은 정보가 투자자들에게 제공되도록 하고, 합병의 타당성과 공정성에 대해 회사가 투자자들에게 적극적으로 설명하도록 하는 것이 필요하다. 특히 합병비율의 구체적 산정근거와 적정성에 대한 이사회의 의견이 반드시 포함되도록 하고 계열사간 합병의 경우 합병이 지분관계 등 중요한 이해관계에 미치는 영향을 공시하도록 하며, 주주들의 이익을 보호하기 위한 조치(독립적 외부평가, 독립위원회의 심의를 통한 합병가액 결정) 등 회사가 취한 공정성 담보방안을 함께 공시하도록 하는 방안도 고려하여야 한다.
3. 주주의 이익을 해할 우려가 있는 합병의 공정성 담보 방안
합병가액 산정방식 등에 대한 내용이 구체적으로 사전에 공시된 경우, 주주들이 이를 확인하고 불이익을 입을 우려가 있으면 문제제기할 수 있는 추가적인 방안을 마련할 필요가 있다. 이를 위해 해외 주요국의 입법례에서 인정하고 있는 합병유지청구권, 합병검사인제도, 합병관계자의 손해배상책임을 도입할 것을 제안한다. 다만 모든 합병에 이를 적용하는 것이 아니라, 주주의 이익을 해할 우려가 있을 경우 주주의 요청에 의해 행사할 수 있도록 제도를 설계하도록 하는 것이 필요하다. 특히 1명의 주주가 요청할 경우 허용되는 단독주주권이 아니라 일정 지분율 이상의 주주가 요구할 때 인정되는 소수주주권으로 도입하여야 한다. 사실상 합병의 불공정에 대한 문제가 제기되는 사례는 적은데, 이를 모든 합병에 요구한다면 도리어 합병이 저해되고 일부 주주의 문제제기로 대다수 주주가 피해를 입는 부작용이 우려되기 때문이다.
가. 합병유지청구권 도입
합병가액 산정방식이 사전에 공시된 경우, 주주들이 이를 확인하고 불이익을 입을 우려가 있으면 유지청구권을 행사할 수 있도록 합병유지청구권을 도입하는 것이 필요하다.33) 현행 상법에서는 이사가 법령 또는 정관에 위반한 행위를 하여 이로 인하여 회사에 회복할 수 없는 손해가 생길 염려가 있는 경우에만 유지청구권을 허용하는데(제402조), 합병에서 회사의 손해와 주주의 손해는 다를 수 있어 주주가 유지청구권을 행사하는데 한계가 있다. 이에 일본에서는 회사법을 개정하여, 합병 등의 조직재편시 주주들이 사전적으로 유지청구권을 행사할 수 있도록 규정하였다(제796조의2). 주주가 불이익을 받을 염려가 있을 때에는 주주는 회사에 대해 합병을 중지할 것을 청구할 수 있다. 미국의 경우에도 주주가 유지명령청구권을 행사할 수 있다.34) 해당 합병거래가 사기적이거나35) 주식의 저평가와 관련하여 반대 소수주주에게 명백하게 해를 주는 재량권의 남용, 신뢰위반, 임무해태와 같은 문제가 있는 경우36)에도 유지명령청구가 허용된다.
나. 합병검사인제도
현행 상법에서는 총회검사인37)이나 현물출자검사인38)제도를 두고 있는데, 소수주주권으로 합병검사인제도를 도입하는 것을 검토할 수 있다.39) 합병가액의 산정은 회사들이 자율적으로 정하도록 하되, 회사가 정한 합병비율과 판단근거가 적정한지를 객관적이고 전문성 있는 제3자가 검토하도록 한다면 합병가액 및 절차의 공정성을 담보하는데 기여할 수 있을 것이다.40) 독일의 경우 완전모자회사간 합병이 아닌 이상, 합병계약에 합병검사인의 선임을 의무화하고 있다(조직재편법 제9조 및 제10조). 합병검사인은 대표이사의 신청에 따라 법원에 의하여 선출되고 임명되며, 합병비율의 산정방법 및 그 적정성, 복수의 평가방법이 사용되었다면 평가방법별로 어떠한 합병비율이 산정되었고 어떤 가중치를 부여하였는지 등을 평가하고 서면으로 보고서를 작성하여 주주총회 전에 제출한다(조직재편법 제12조). 다만 주주총회 전까지 신속한 검토를 위해, 합병검사인이 직접 합병회사를 평가하는 것이 아니라 회사가 사전에 제출한 자료를 토대로 적정성을 평가한다. 이러한 합병검사보고서는 합병비율의 공정성을 담보하는 수단으로 실무에서 상당히 성공적인 것으로 평가받고 있다.41)
다. 합병 관계자의 손해배상책임 인정
우리 상법에서는 이사의 손해배상책임을 인정하지만, 유지청구권과 마찬가지로 회사에 손해가 발생한 경우에만 책임을 지게 된다(제399조).42) 그런데 합병과 같은 조직재편에서 회사의 손해와 주주의 손해는 다를 수 있고 특히 지배주주와 소수주주간 이해상충으로 소수주주에게만 손해가 발생한 경우에는 이사에 대해 책임을 추궁하기 어렵다. 이러한 문제를 인식하고 독일에서는 소멸회사의 경영진에게 합병비율을 결정할 때 주주가 손해를 입지 않도록 주의를 기울이도록 하고, 주의의무를 소홀히 하여 소멸회사의 주주가 손해를 입으면 주주는 이사를 상대로 직접 손해배상을 청구할 수 있도록 하고 있다(조직재편법 제25조).43) 합병과 같은 조직재편에서 이러한 손해배상책임을 도입하는 것도 소수주주를 보호하고 합병의 공정성을 담보할 수 있는 대안이 될 수 있다. 외부평가기관의 선임과정에서 위법이 있을 경우 선임기관에 대한 손해배상책임을 인정하고, 외부평가기관의 평가와 관련하여 외감법 제31조44)나 자본시장법 제125조45)와 같은 손해배상책임을 규정하도록 한다. 독일식 합병검사인제도가 도입된다면, 합병검사인의 손해배상책임 규정도 함께 마련하여야 한다.
Ⅳ. 나가며
시장주가를 기준으로 산정하는 합병가액 산정방식이 관행으로 자리잡았으나, 시장주가에 의존한 합병가액 산정방식과 합병시점의 임의성, 합병가액의 불확실성 등의 문제로 인해 당초 입법목적과 달리 투자자 보호에 기여하지 못하고 있는 현실이다. 또한 합병가액에 대한 규제가 도입될 당시와 MSCI 선진국지수의 편입을 도전하는 현재의 자본시장이 다르다는 점에 비추어 볼 때도 제도 개선의 필요성이 요구된다. 1990년대는 자본시장의 규모가 작았고 자본시장의 인프라도 발달하지 않아서 감독당국이 후견적 역할을 하였으나, 이제는 합병가액의 적절성과 공정성에 대해 회사가 제공한 정보를 토대로 하여 시장에서 이해관계자들이 평가할 수 있도록 하는 것이 적절하다.
합병가액을 자율화하되, 계열사간 합병과 비계열사간 합병을 나누지 않는 방향으로 추진해야 한다. 기업가치를 토대로 하는 합병가액의 산정방식은 동일하게 하되, 이해관계자간 거래의 경우 합병가액 산정과 합병절차의 공정성을 강화하는 방안으로 추진하는 것이 바람직하다. 지금까지는 법에서 합병가액 산정방식을 정하고 있었으니 회사 입장에서 그 적정성이나 타당성을 적극적으로 주장하지 않았으나, 이를 자율화할 경우 계열사간 합병에서 회사는 공정성을 더 입증하려 할 것이다. 계열사간 합병의 경우 시장은 대주주의 영향력에 대해 관심을 가지고 볼 것이기 때문에, 주주총회에서 주주들의 찬성을 얻기 위해 그리고 유지청구권이나 합병검사인 등의 소수주주권 행사를 피하기 위해 회사는 더 적극적으로 합병가액의 적정성과 타당성을 입증하려 할 것이다. 이러한 합병가액의 자율화 및 공시강화, 주주의 이익을 해할 우려가 있는 합병의 공정성 담보를 위한 제도 개선이 실질적인 투자자 보호와 자본시장에 대한 신뢰도 향상에 기여할 것으로 기대한다.
1) 금융위원회(2023. 5. 8)
2) 독일의 경우 증권취득 및 인수에 관한 법률에 의해 공개매수시 인수자의 제안 직전 3개월 이내의 거래량 가중평균주가 및 최근 6개월간 있었던 다른 제안가격 중 가장 높은 가격으로 정하도록 규제하나, 이는 합병하는 회사가 자율적 협의로 정하는 합병가액과는 다르다.
3) 합병에는 흡수합병과 신설합병이 있으나, 우리나라의 경우 신설합병이 매우 드물고 흡수합병이 대부분이기에 흡수합병을 기준으로 합병의 정의를 설명하였다.
4) 합병에 반대하는 주주에게 주식매수청구권이 인정되나, 이는 회사에 남지 않겠다는 주주들의 주식을 회사가 매수해 주는 제도일 뿐 회사에 계속 머물면서 정당한 주식가치를 보장받기 원하는 주주들을 보호할 수 있는 제도는 아니다.
5) 2009년 증권거래법이 폐지되면서 합병 관련 규정이 자본시장법으로 이관되었다.
6) 가중평균 계산 시 가중치는 거래량으로 한다.
7) 김건식(2015, p.86), 송옥렬(2023, p.1244)
8) 김희준(2015, p.352)
9) 김홍기(2011, pp.181-182)
10) 권기범(2011, p.155)
11) 주권상장법인은 공개시장에서 다수 투자자들의 자유로운 거래에 의하여 그 주가가 형성되는 것이어서 공개시장에서 형성된 주가가 해당 상장법인의 일정시점에 있어서의 가치를 비교적 객관적으로 반영한다고 볼 여지가 있는 점 등을 고려하여 합병에 있어 핵심적인 요소인 합병가액을 미리 법령에서 마련한 일정한 방식에 의하도록 하면서 그 구체적 사정에 있어서는 비교적 객관적 기준이라 볼 여지가 있는 공개시장의 주가를 기준으로 삼도록 한 것이다(서울고등법원 2015. 7. 16 자 2015라20485 결정).
12) 미국과 일본의 실제 거래액을 비교할 때는 ‘합병가액’이 아니라 ‘합병액’이라는 용어를 사용하고자 한다. ‘합병가액’은 1주당 가격인 반면, ‘합병액’은 발행주식총수를 곱한 전체 거래액으로, 전체 합병규모를 정확하게 비교하기 위해 ‘합병액’이라는 용어로 사용한다. 즉 본 보고서에서 사용한 합병액은 합병가액 × 발행주식총수이다.
13) 블룸버그 데이터를 이용하여 분석을 시행했는데, 블룸버그에서는 기업의 인수합병이 발생한 경우, 존속회사와 소멸회사의 이름, 인수합병이 발표된 날짜, 성사된 인수합병의 가치(Announced total value), 소멸회사의 TV/EBITA 등의 정보를 제공한다. 이 중 2019년 1월에서 2023년 4월까지 상장법인간 인수합병이 발표된 데이터를 추출하였다. 블룸버그에서는 해당 거래가 합병(merger)인지 인수(acquisition)인지는 구분하지 않고 있어, 인수합병이 발생한 이후 150일 거래일 내에 소멸회사가 상장폐지된 경우를 합병으로 간주해 분석에 이용하였다. 분석의 편의를 위하여 존속회사와 소멸회사가 모두 미국기업인 경우로 제한하였다.
14) 기업의 시장가격과 실제 합병액과 자본시장법에 따른 합병액의 차이의 절대값을 기업의 시장가격으로 나눈 값은 약한 음의 상관관계(-0.0542)를 보이나, 통계적으로 유의한 수준은 아니다.
15) 일본의 경우 존속회사가 합병 이전에 이미 소멸회사의 주식을 취득하고 있는 경우가 존재하였고(계열사간 합병 포함), 해당 경우 블룸버그에는 추가로 취득하는 주식의 가격이 거래가격으로 기록하였다. 자본시장법상의 합병가액과의 적절한 비교를 위하여, 블룸버그에 공개된 거래 가격 대신, EDINET에 공시된 주식매수청구권의 가격 및 언론 보도자료를 참고한 소멸회사 거래가격을 분석에 이용하였다. 분석에 사용된 합병은 존속회사와 소멸회사가 모두 일본기업인 경우로 제한하였다.
16) 기업의 시장가격과 실제 합병액과 자본시장법에 따른 합병액 차이의 절대값을 기업의 시장가격으로 나눈 값은 약한 음의 상관관계(-0.0359)를 보이나, 통계적으로 유의한 수준은 아니다.
17) 손창완(2019, p.284)
18) 자본시장법은 계열사간 합병의 경우 기준시가의 10% 내, 비계열사간 합병의 경우 30% 내에서 합병가액의 할인 또는 할증이 가능하다고 규정하고 있으나, 할증 혹은 할인이 적용된 사례는 전무하였다. 따라서 합병가액에 대해 외부평가기관의 평가를 받는 경우도 나타나지 않았다.
19) 2018년부터 2022년까지 상장법인간 합병 중, 합병 발표 시점 1년전 시장에 상장된 29개 기업의 합병 발표 1년 전부터 합병 발표일까지 1년 누적 시장조정수익률의 평균값이다.
20) 권기범(2011, pp.171-173)
21) 대법원 2010. 7. 22. 선고 2008다37193 판결(이랜드·이랜드월드 분할합병 사건), 대법원 2009. 4. 23. 선고 2005다22701,22718 판결(국민은행·한국주택은행 합병 사건), 대법원 2008. 1. 10. 선고 2007다64136 판결(남한제지·풍만제지 합병 사건)
22) 삼성물산과 제일모직의 합병에 대한 합병무효의 소는 서울고등법원에서 2심 중에 당사자가 항소를 취하하였다(2022. 5.).
23) 김지환(2017, p.335), 최민용(2017, p.146)
24) 노혁준(2016, p.97)
25) 노혁준(2016, p.88)
26) 김건식(2015, p.87)
27) 미국의 경우에도 계열사간 합병에서는 강화된 공정성을 요구하고 있는데, 2014년 델라웨어 주에서는 Kahn v. M&F Worldwide Corp. 판결에서 특별이해관계자와의 합병에서 사외이사로 구성된 독립적인 특별위원회와 소수주주의 과반수가 모두 승인한다면 공정성이 추정되어 경영판단원칙이 적용된다고 판시하였다.
28) 노혁준(2016, p.131)
29) 정형찬(2019, p.189)
30) SEC는 주요사항보고서(8-k)로 합병에 대한 결정을 공시하도록 하고 있고, 합병결정 공시이후 SEC에 합병 위임장을 제출하도록 한다(DEFM14A). 합병 위임장은 합병에 대한 주주총회 이전에 합병계약 관련 구체적 정보를 주주들에게 제공하는 서류인데, 예비위임장(PREM14A)을 먼저 제출하고 최종 위임장(DEFM14A)을 제출하기도 한다. 합병 또는 교환 제안의 일부로 신주가 발행되는 경우 취득자는 취득자의 주주가 주식 발행을 승인하도록 요청하는 등록 명세서(S-4)를 제출하도록 한다.
31) 합병비율을 산출하는데 사용한 방법 또는 복수의 방법을 표시하고 해당 방법이 합리적인지에 대한 의 견과 합병비율이 합리적인지 여부를 기재하여야 한다. 이를 위해 합병회사의 모든 해당 서류에 대한 접근권과 회사 임원에 대하여 합병 관련 정보의 요구권을 갖는다(회사법 제909조).
32) 각 회사의 기업가치 산정에서 독립된 제3자의 외부평가를 받은 내용, 이해관계자를 가진 이사를 합병결의에서 제외한 것, 사외이사 또는 독립위원회에서 심의하여 합병대가를 결정한 것 등의 주주 보호 조치에 대해 회사가 설명하도록 하고 있다.
33) 김지환(2017, p.337)
34) 황현영(2012, p.38)
35) Young v. ValhiInc., 382 A 2d 1372 (Del. Ch. 1978)
36) In Cole v. National Gas Credit Corp., 156A. 2d 187-188 (Del. Ch. 1931)
37) 상법 제367조(검사인의 선임) ① 총회는 이사가 제출한 서류와 감사의 보고서를 조사하게 하기 위하여 검사인(檢査人)을 선임할 수 있다. ② 회사 또는 발행주식총수의 100분의 1 이상에 해당하는 주식을 가진 주주는 총회의 소집절차나 결의방법의 적법성을 조사하기 위하여 총회 전에 법원에 검사인의 선임을 청구할 수 있다.
38) 상법 제299조(검사인의 조사, 보고) ① 검사인은 제290조 각 호의 사항과 제295조에 따른 현물출자의 이행을 조사하여 법원에 보고하여야 한다.
39) 노혁준(2016, p.107)
40) 합병절차의 공정성 담보를 위해 소수주주의 다수결을 도입하자는 의견도 있으나, 이는 미국에서 회사가 자신들이 추진하는 합병의 공정함을 입증하기 위해 자발적으로 채택한 방안 중 하나로 법에서 이를 강제하는 것은 적절하지 않다고 본다. 즉 회사가 자발적으로 소수주주의 다수결 절차를 거쳤다면 합병이 공정하다고 볼 수 있는 근거가 될 뿐이다.
41) 정대익(2018, p.322)
42) 상법 제401조에 의해 주주의 직접손해에 대한 이사의 손해배상책임도 인정이 되지만, 합병과 같은 조직재편에서 주주의 손해는 직접손해가 아닌 간접손해이기 때문에 보호받지 못한다.
43) 다만 독일의 경우 존속회사의 주주들은 존속회사의 이사를 상대로 손해배상책임을 추궁할 수 없고, 소멸회사의 주주들만 가능하다.
44) 외감법 제31조(손해배상책임) ① 감사인이 그 임무를 게을리하여 회사에 손해를 발생하게 한 경우에는 그 감사인은 회사에 손해를 배상할 책임이 있다. ② 감사인이 중요한 사항에 관하여 감사보고서에 적지 아니하거나 거짓으로 적음으로써 이를 믿고 이용한 제3자에게 손해를 발생하게 한 경우에는 그 감사인은 제3자에게 손해를 배상할 책임이 있다. 다만, 연결재무제표에 대한 감사보고서에 중요한 사항을 적지 아니하거나 거짓으로 적은 책임이 종속회사 또는 관계회사의 감사인에게 있는 경우에는 해당 감사인은 이를 믿고 이용한 제3자에게 손해를 배상할 책임이 있다.
45) 자본시장법 제125조(거짓의 기재 등으로 인한 배상책임) ① 증권신고서(정정신고서 및 첨부서류를 포함한다. 이하 이 조에서 같다)와 투자설명서(예비투자설명서 및 간이투자설명서를 포함한다. 이하 이 조에서 같다) 중 중요사항에 관하여 거짓의 기재 또는 표시가 있거나 중요사항이 기재 또는 표시되지 아니함으로써 증권의 취득자가 손해를 입은 경우에는 다음 각 호의 자는 그 손해에 관하여 배상의 책임을 진다. 다만, 배상의 책임을 질 자가 상당한 주의를 하였음에도 불구하고 이를 알 수 없었음을 증명하거나 그 증권의 취득자가 취득의 청약을 할 때에 그 사실을 안 경우에는 배상의 책임을 지지 아니한다.
참고문헌
고봉찬ㆍ김진우, 2023, 기업가치 평가 관련 규정과 현금흐름할인법의 도입 필요성, 『한국 증권학회지』52(2), 301-329.
권기범, 2011, 『기업구조조정법(제4판)』, 삼영사.
권재열, 2015, 삼성물산 대 엘리엇 결정 – 주요쟁점의 재검토, 『상사판례연구』 28(4), 3-54.
금융감독원, 2009. 6. 23, 자산평가의 공정성 확보를 위한 「외부평가업무가이드라인」 제정, 보도자료.
금융위원회, 2023. 5. 8, 기업 M&A 지원방안, 보도자료.
김건식, 2015, 삼성물산 합병사례를 통해 본 우리 기업지배구조의 과제, 『BFL』 74, 83-101.
김배정, 2015, 합병비율의 공정성을 위한 제언, 『법학연구』 56(4), 163-192.
김지환, 2017, 주식매수청구권에 대한 재검토, 『상사법연구』 36(2), 307-346.
김홍기, 2011, 현행 주식가치평가의 법적 쟁점과 ‘공정한 가액’에 관한 연구, 『상사법연구』 30(1), 159-205.
김희준, 2015, 상장법인 간 합병에 적용되는 합병비율 산정방식 검토 - 삼성물산과 제일모직의 합병사례를 중심으로, 『상사법연구』 34(3), 331-366.
노혁준, 2016, 합병비율의 불공정성과 소수주주 보호 – 유기적 제도설계를 향하여 –, 『경영법률』 26(2), 87-138.
손창완, 2019, 상장회사 합병과 합병비율의 공정성 – 관련 규정 및 사례에 대한 비판적 검토, 『상사법연구』 38(3), 235-296.
송옥렬, 2023, 『상법강의(제13판)』, 홍문사.
임재연, 2008, 『증권거래법(전정판)』, 박영사.
정대익, 2018, 합병비율 불공정에 대한 독일의 사후적 구제수단, 『금융법연구』 15(3), 317-365.
정형찬, 2019, 합병비율 산정에 관한 자본시장법 시행령의 개정 방향, 『경영법률』 29(4), 155-200.
최민용, 2017, 계열사 간의 합병과 회사법적 규제, 『상사판례연구』 30(3), 115-161.
최성근, 2019, 상법과 자본시장법의 주식평가방법에 대한 해석론 및 입법론, 『상사법연구』 38(1), 179-220.
최순영ㆍ김종민, 2018, 『기업 소유구조가 국내 상장사 간 합병에 미치는 영향 분석』, 자본시장연구원 연구보고서, 18-02.
황현영, 2012, 상법상 강제매수제도에 관한 연구, 한양대학교 대학원 박사학위 논문.
황현영, 2013, 회사의 조직재편시 공정한 주식가치평가에 대한 제언, 『법과 정책연구』 13(1), 65-87.
기업의 M&A는 기업의 성장·혁신을 촉진하고 경제의 역동성을 제고하는 중요한 수단이고, 최근 글로벌 환경변화에 따라 M&A의 중요성은 더욱 증대되고 있다. 정부에서도 2023년 5월 기업 M&A 지원방안을 발표하면서, 오랫동안 문제로 지적되어 온 합병가액 산정방식에 대한 개선방안을 제시하였다. 합병 공시강화, 외부평가기관 규율 마련을 전제로 비계열사간 합병가액 산정 방법을 자율화하겠다는 방침이다. 다만 계열사간 합병의 경우 비계열사간 합병가액 산정방법 자율화에 따른 시장 영향 등을 보아가며 중장기 검토하겠다고 발표하였다.1)
합병은 회사라는 재화를 거래하는 것으로, 여타 다른 재화의 거래와 같이 매도자와 매수자 간의 협상력과 거래방식에 따라 가격이 달라질 수 있게 마련이다. 이에 미국, 일본, 영국, 독일2) 등 해외 주요국의 경우 합병가액 및 합병비율의 산정을 합병하는 회사들의 자율적 판단에 맡기고 있다. 한편 우리나라에서는 1997년부터 지금까지 상장법인 간 합병 그리고 상장법인과 비상장법인의 합병시 합병가액의 산정 방법에 대해 법에서 구체적으로 정하고 있다. 합병가액 산정방식을 법에서 정하는 독특한 제도는 우리나라의 자본시장이 미성숙했고 상장법인의 수도 적었던 시기에, 시장의 공정성을 확보하고 투자자 보호를 강화하기 위해 금융당국이 직접 합병비율 조정을 권고하는 등 합병 내용의 실질적 심사를 하면서 시작되었다. 이후 주가를 기준으로 합병가액을 산정하는 것에 대한 비판이 계속되면서, 시장주가의 신뢰성 확보를 위한 개정이 여러 차례 있었으나 구체적인 산식의 변화만 있을 뿐 여전히 법에서 합병가액을 정하는 규제는 지금도 유지되고 있다.
그러나 주가에 의해 획일적으로 산정되는 합병가액은 공정한 합병가액의 산정과 투자자 보호라는 당초 법 제정 목적과는 달리 여러 가지 부작용을 낳고 있는 것으로 판단된다. 이에 본 보고서는 합병가액 산정방식을 법에서 정하는 현행 제도를 유지하는 것이 바람직한가에 대한 문제의식을 가지고, 제도의 문제점을 지적한 후 합병가액을 자율화하되 투자자 보호라는 제도의 본래 취지를 달성하기 위한 추가적 개선방안을 제안하고자 한다.
Ⅱ. 합병가액 산정 관련 현행 제도 및 문제점
1. 합병비율 및 합병가액의 중요성
회사는 대내외 경영환경에 대응하여 다양한 조직재편을 시도하는데, 그 중 대표적인 것이 합병이다. 합병은 2개 이상의 회사가 합병계약을 통해, 소멸회사(피합병회사)의 모든 권리 의무를 존속회사(합병회사)가 이전받고 소멸회사의 주주에게 존속회사의 주식 또는 금전 등의 재산을 교부하는 법률행위이다.3) 이 경우 소멸회사의 주주들에게 합병대가로 존속회사의 주식을 몇 주 교부할 것인지가 중요한데, 그 기준이 되는 것이 합병비율이다. 합병비율은 존속회사의 주식과 소멸회사의 주식의 교환비율이고, 결국 소멸회사의 모든 것을 존속회사에 넘기는 대가로 제공되는 ‘가격’이다. 예를 들어, 존속회사와 소멸회사의 합병비율이 1:0.5인 경우 존속회사의 1주와 소멸회사의 0.5주가 같은 가치라는 의미이고 소멸회사의 주식을 1주 가지고 있는 주주는 존속회사의 주식 0.5주를 받을 수 있게 된다. 합병비율에 따라 주주들이 받게 되는 주식의 수가 달라지므로, 합병비율은 주주들의 이해관계에 직접적인 영향을 미치게 된다.
그런데 합병비율은 합병계약을 체결하는 회사들의 이사회에서 결정되고, 주주는 이미 결정된 합병비율에 대하여 주주총회에서 찬성 혹은 반대의견을 낼 수 있을 뿐, 합병비율 결정에 직접적으로 관여하지는 못한다.4) 따라서 이사회와 주주 간, 혹은 주주들 간의 이해관계가 다를 경우 일부 주주에게 불리한 합병비율로 합병이 진행될 가능성이 있다. 이러한 문제점을 보완하고 주주의 이익을 보호하기 위하여, 우리 법제는 공정한 합병비율을 보장하기 위한 합병가액 산정에 관한 규정을 마련하고 있다. 합병가액은 합병비율을 산정하는 근거로, 존속회사와 소멸회사의 합병가액의 비율이 합병비율이 된다. 예를 들어, 존속회사의 합병가액이 2만원, 소멸회사의 합병가액이 1만원인 경우, 합병비율은 2만원:1만원, 즉 1:0.5가 된다. 자본시장법은 상장법인의 경우 주가를 기준으로, 상장법인과 합병하는 비상장법인의 경우 자산가치와 수익가치를 기준으로 합병가액을 산정하도록 규정하고 있다.
2. 현행법상 상장법인의 합병가액 산정방법
가. 상장법인에 대한 합병 관련 규제의 입법취지와 연혁
1962년 증권거래법(법률 제972호, 1962. 1. 15, 제정)이 처음 제정되었을 당시에는 상장법인의 합병과 관련하여 특별한 규제가 없었으나, 1976년 증권거래법(법률 제2920호, 1976. 12. 22, 전부개정)을 전면적으로 개정하면서 상장법인이 비상장법인과 합병하는 경우, 비상장법인에 대하여 합병승인을 위한 주주총회일 6월 전에 증권관리위원회에 등록하도록 하였다(제3조). 더불어 합병계약승인결의시 상장법인에 대하여 이를 증권관리위원회와 거래소에 신고하도록 하였다(제186조 제7항).
그러나 합병사실을 신고하는 것만으로는 합병의 공정성이나 타당성을 판단하는데 필요한 정보를 투자자들에게 충분히 제공할 수 없다는 문제가 제기되었고, 이에 1991년 증권거래법(법률 제4469호, 1991. 12. 31, 일부개정)을 개정하여 합병신고제도를 도입하였다(제190조의2). 합병신고제도의 도입 이후 증권관리위원회에서는 합병신고서를 검토하면서 합병의 보류, 합병비율 조정의 권고 등 상장법인 합병의 실질적 내용에 관한 규제를 하였고, 1997년 증권거래법(법률 제5254호, 1997. 1. 13, 일부개정) 개정을 통해 합병가액 등 합병 요건 및 절차에 대한 규제를 도입하였다. 도입 당시에는 주권상장법인(유가증권시장 상장법인)에 대해서만 규제하였으나 이후 협회등록법인(코스닥시장 상장법인)에도 적용하여 규제 범위는 확대된 반면, 합병가액을 산정하는 구체적인 산식의 변화만 있을 뿐 법에서 합병가액을 정하는 규제는 지금도 유지되고 있다.5)
나. 상장법인 합병가액 산정기준의 변화
주가를 기준으로 합병가액을 산정하는 것에 대한 비판이 계속되면서, 시장주가의 신뢰성 확보를 위한 개정이 여러 차례 있었다. 합병신고서 제출 전일을 기준으로 주가를 산정하던 기준을 이사회 결의일 또는 합병계약 체결일 중 앞서는 날의 전일로 하여 합병이 주가에 미치는 영향을 최소화하고자 하였다. 또한 제도의 도입당시에는 1개월간의 최종시세가격만을 기준으로 산정하였으나 이후 최근 1개월간의 종가 및 거래량을 이용하여 가중 평균한 값을 기준으로 기준시가를 산출하고6), 할인 또는 할증할 수 있도록 하는 재량권도 허용하였다.


현행법상 상장법인의 합병가액은 합병에 대한 이사회 결의일 또는 계약체결일 중 빠른 날의 전일을 기산일로 하여 과거 1개월, 1주일, 직전일의 종가를 거래량으로 각각 가중평균한 후 산술평균한 값을 기준시가로 하여, 비계열사간 30%, 계열사간 10%의 범위에서 할인 또는 할증할 수 있도록 정하고 있다. 다만 비계열사가 10%를 초과하여 할인 또는 할증하거나 계열사가 기준시가를 초과하여 할인 또는 할증하는 경우 외부평가기관의 평가를 의무적으로 받아야 한다. 상장법인과 비상장법인의 합병시 상장법인은 기준시가를 기준으로 하되 기준시가가 자산가치에 미달할 경우 자산가치를 적용할 수 있도록 하고, 비상장법인은 자산가치와 수익가치를 각각 1과 1.5로 가중평균하여 산정한 본질가치를 합병가액으로 하도록 한다(자본시장법 시행령 제176조의5).
이러한 합병기준이 실무에서는 사실상 강제되는데, 이를 준수하지 않으면 금융감독원에서 존속회사가 제출하는 증권신고서를 자본시장법 제120조 제2항에 근거하여 수리하지 않기 때문이다.7) 법에서 획일적인 산정기준을 정해줌으로써 합병가액 산정의 신속성과 비용부담 절감 등에 기여하였고8), 신뢰할 수 있는 거래소 주가를 통해 평가자의 의문을 최소화하고 예측가능성을 제고하였다는 긍정적 평가도 있다.9) 그러나 합병거래의 조건을 당사자의 자율적 교섭에 의하지 않고 법에서 정하도록 함으로써 당초 입법취지와 달리 투자자들에게 부정적인 영향을 끼치고 있다는 문제도 지적되고 있어 아래에서는 이 부분을 자세히 살펴보고자 한다.
3. 상장법인 합병가액 산정방식의 문제점
가. 시장주가에 의존한 획일적 산정방식
이론상 가격은 시장에서 평가된 기업의 가치를 반영한다는 점에서 합병가액 산정의 타당한 근거가 될 수 있다. 그러나 가격은 기업의 내재가치 이외의 다른 요인들에 의해서 매일 변동하게 마련이다. 회사가 합병을 결정할 때는 회사의 시장주가도 중요한 기준이 될 수 있지만 합병으로 인한 당사 회사의 상호보완성 및 시너지 효과, 회사의 연구개발인력의 자질, 경영진의 자질 같은 무형의 자산들도 중요하게 여겨질 수 있다.10) 이러한 이유로 자본시장이 발달한 미국, 영국, 일본 등 주요국에서도 합병가액 및 합병비율의 산정을 합병하는 회사의 자율적 판단에 맡긴다.
초기 미국의 판례를 보면 시장가치법에 의하여 주식가격을 결정하는 입장이었는데 시장가치의 신뢰성에 대한 문제가 제기되면서, 1980년 델라웨어주는 Bell v. Kirby Lumber Co. 판결에서 시장가치, 자산가치, 수익가치를 가중평균하는 방법으로 주식의 가치를 산정하였다. 이는 델라웨어 가중평균법으로 불리우며, 이후 다른 주 법원의 판결에 영향을 미쳤다. 델라웨어주 대법원은 1983년 이른바 Weinberger v. UOP. 판결에서, 그동안 사용했던 델라웨어 가중평균법을 탈피하고 새로운 주식가격산정방법으로 현금흐름할인법(DCF)을 제시하였다. 이후 현금흐름할인법이 많이 활용되었으나, 2017년 DFC Global Corp. v. Muirfield Value Partners, L.P 판결에서는 거래가격이 가장 믿을 수 있는 가치라고 판단하기도 하였다. 일본의 경우 합병비율은 존속회사와 소멸회사의 경영진이 합의한 주식 및 기업가치 평가액에 근거하여 산정하는데, 일본의 최근 5년간 합병공시를 검토한 결과, 시장주가법과 현금흐름할인법이 가장 많이 쓰였고 그 외에 유사기업 비교법 정도를 사용하고 있다.
법에서 합병가액 산정방식을 정한 주요 목적은 투자자 보호이다. 법원은 자본시장법 시행령에서 정한 합병가액의 입법취지를 “주권상장법인의 경우 수많은 투자자들이 관련되어 있어서 합병가액을 규제함으로써 투자자를 보호할 필요성이 높기 때문”이라고 해석한다.11) 현행법에 따른 합병가액 산정이 획일적이라 하더라도 투자자 보호라는 당초 입법취지를 달성하고 있다면 큰 문제가 되지 않을 것이다. 그러나 미국과 일본의 합병에서 실제로 거래된 합병가액과 국내의 기준시가 산정방식으로 도출한 합병가액을 비교한 결과, 국내의 합병가액 산정방식이 당초 입법취지와는 다르게 작용하고 있는 것으로 보인다.
2019년 1월부터 2023년 4월까지 미국의 상장법인간 합병 총 333건에 대하여 우리나라 자본시장법에 따라 소멸회사의 기준시가를 산출해 실제 거래된 합병액12)과 비교하였다.13) 아래 <표 Ⅱ-2>를 보면 실제 발표된 미국 상장회사의 합병가액이 우리나라 자본시장법에 따른 기준시가 이상인 경우가 전체의 86.2%(287건)에 달했다. 기준시가를 10% 할증한 가격 이상으로 거래된 경우는 77.2%(257건), 기준시가를 30% 할증한 가격 이상 거래된 경우도 56.8%(189건)으로 우리나라 자본시장법상 합병가액으로 허용될 수 있는 가격보다 훨씬 더 높은 가격으로 합병이 성사되는 것으로 나타났다.

아래 <그림Ⅱ-1>은 조사 대상 기업들의 실제 거래액과 우리나라 자본시장법에 따라 산출한 합병액을 비교한 것이다. 아래 그림을 보면 자본시장법에 따른 합병액이 유사한 기업들간에도 실제 발표된 합병액에는 차이가 존재하는 것을 볼 수 있다. 기업의 시가총액 규모가 유사해 주가에 근거한 합병액은 유사하게 산출된다 하더라도, 기업간의 이질성으로 인해 합병에서 평가되는 소멸회사의 가격은 달라질 수 있는 것이다.
또한 시가총액이 높은 기업일수록 실제 거래액과 합병액의 괴리가 상대적으로 적은 것으로 나타났다. 규모가 작은 기업의 경우, 시장에서 공유되지 않은 기업의 내재가치 정보, 기업의 잠재력, 성장가능성 등이 합병가액의 결정요소로 작용해, 주가를 이용해 산출하는 자본시장법상의 합병가액과 실제 거래액의 차이가 크게 나타났을 수 있다. 반면 시가총액이 높은 기업은 시장에서 기업의 가치가 충분히 판단되었고, 가격에 반영되지 않은 내재가치가 적어 자본시장법상의 합병가액과 실제 합병가액의 괴리가 상대적으로 적게 나타난 것이라고 해석할 수 있다.14)



합병가액 산정방식을 법에서 정하고 있다 보니 합병 관련 기관들의 도덕적 해이도 발생한다. 합병가액 산정에 있어 주주의 이익에 부합하도록 최선을 다해야 하는 이사회도 회사의 진정한 경제적 가치를 측정하고 더 나은 합병 조건을 협상하기 위한 노력을 기울일 필요가 없게 된다. 또한 타인의 자산을 수탁받아 운용하는 연금이나 투자펀드 등의 기관투자자에게도 현행의 제도는 투자 대상인 합병 기업의 경제적 가치를 평가하여 적절한 조치를 취할 의무를 사실상 면제하고 있다. 합병가액에 대해 평가하는 회계법인 역시 법에서 정한 산식을 준수하였는지 여부만 판단하면 되는 것이 현실이다. 이러한 점을 종합할 때 시장주가에 의존한 획일적 산정방식은 투자자 보호라는 당초 입법취지를 달성하지 못하고 있는 것으로 판단된다.
나. 합병시점의 임의성
시장주가를 해당 기업의 객관적 가치가 반영된 가격으로 신뢰할 수 있는 경우에도, 합병시점의 선택에 있어서는 소수주주보다 지배주주의 의견이 더 크게 반영될 수 있다는 문제가 제기될 수 있다. 2018년부터 2022년 12월말까지 발표된 모든 상장사간 합병(16건)을 살펴본 결과, 합병가액은 모두 자본시장법에 따른 기준시가로 결정되었다.18) 해당 기간 존속회사와 소멸회사의 주가수익률을 보면, 합병 발표 1년 전부터 누적 시장조정수익률은 –16.0%로 나타났다. 이는 합병시점이 소수주주에게 불리하게 선택되었을 가능성이 있음을 시사한다.19) 대법원에서도 2015년 삼성물산과 제일모직 합병 승인 이사회 직전 삼성물산 주가는 회사의 적정가치를 표시하지 못한다고 판단하면서, 주식매수가격의 기준시점을 합병일이 아닌 제일모직의 상장 전일로 하여 주가를 산정하도록 결정하였다(대법원 2022. 4. 14. 자 2016마5394 결정).
이러한 실제 사례들을 보면서 투자자들은 일정 시점의 주가를 신뢰하기 어렵게 되고, 합병가액의 공정성에 대한 문제를 제기하게 된다. 지배주주가 시세조종 등 별다른 위법행위를 하지 않더라도, ‘합병의 시점’을 선택할 수 있다 보니 소수주주에게 불리한 시기에 합병할 수 있는 가능성이 있다. 더욱이 현재 우리나라 상장법인 간 합병은 모두 계열사간 합병인데, 의도적으로 일방 계열회사의 주가를 띄우거나 억누를 가능성이 있으므로, 시가는 정확한 잣대가 되지 아니한다는 비판도 있다.20)
그러나 합병비율이 불공정해도 법에서 정한 산식대로 했다면 주주들은 합병 무효의 소송을 제기하기 어렵고 실질적으로 구제를 받을 수도 없다. 합병의 무효는 실제 사건화된 경우가 매우 적어 합병무효에 관한 대법원 판결은 3건21)에 불과하고22), 법에서 정한 합병가액 산정방식을 따른 이상 합병비율의 현저한 불공정으로 인한 합병무효는 인정되지 않았다. 법에서 합병가액의 산식을 규정하고 있기 때문에 법원은 합병비율이 공정한지에 대해 면밀히 판단하지 않으며, 불공정의 입증책임도 오로지 원고의 부담으로 작용한다.23) 그런데 소수주주 입장에서는 회사 내부의 사정에 대해 정확히 알지 못하고, 회사가 진행 중인 사업에 대한 정보가 제한적이므로 지배주주 또는 경영진 주도하에 은밀하게 이루어지는 주가에 대한 영향력 행사(특히, 의도적인 경영부진으로 인한 주가하락)를 입증하기가 쉽지 않다.24) 결과적으로 법에서 정한 합병비율이 합병의 불공정으로부터 주주들을 보호해 줄 수 없게 만들 뿐 아니라, 합병 시점이 적절한가에 대한 투자자들의 불신을 초래하는 문제가 있다.
다. 합병가액의 불확실성
우리나라의 경우 상장법인간 합병은 거의 이루어지지 않는데, 최근 5년간 주권상장법인의 합병 총 520건 중, 상장법인간 합병은 16건으로 전체 3.1%에 불과하다. 또한 이 16건은 모두 계열사간 합병으로, 독립적인 당사자에 의한 합병인 비계열사간 합병은 전무하다. 최순영·김종민(2018)에서도, 1999년에서 2016년 사이 금융회사를 제외한 상장사 간의 합병 106건 중 존속회사와 소멸회사가 서로 독립적인 경우는 10건(9.4%)으로 조사한 바 있다.

회사의 구체적 상황에 따라 회사의 가치평가 방법은 다양할 수 있는데, 법에서 정한 획일적 기준을 적용하므로 당사자 사이의 협상 여지를 차단하게 되고 심한 경우 거래를 가로막을 수도 있다. 뿐만 아니라 이사회 결의일 전일의 시장 주가에 따라 합병가액이 달라지는 불확실성으로 인해 회사는 합병을 주저할 수 있다. 결과적으로 회사 입장에서 보면 현행법상 합병가액 산정기준으로 인해 합병을 선호하지 않게 되고, 회사의 자유로운 M&A 거래를 저해하는 문제가 발생하게 된다. 회사가 M&A를 통해 새로운 사업에 진출하고 규모의 경제를 이루어 기업가치를 극대화하는 것은 투자자에게도 긍정적으로 작용할 수 있는 것으로, 이러한 기회가 제한되는 것은 투자자에게 부정적 영향을 미치는 것이라 볼 수 있다.
Ⅲ. 합병가액 산정 관련 제도 개선 방안
1. 합병가액 산정방식의 완전 자율화
회사가 자율적으로 다양한 가치를 고려하여 합병비율을 산정하되, 그렇게 산정한 이유와 그 비율의 공정성을 회사가 입증하도록 하여 시장의 평가를 받게 제도를 설계하는 것이 필요하다. 해외 주요국의 입법례에 비추어 볼 때도 합병가액 산정방식을 직접 법에서 규제하는 것보다 합병하는 회사의 경영진이 공정한 합병비율을 도출할 수 있도록 간접적인 규제방식을 채택하는 것이 바람직하다. 합병하는 회사의 이사회가 회사의 이익에 부합하도록 최선을 다해 협상하여 합병비율을 선정하고, 산정방식과 합병가액의 적정성에 대한 이사회의 의견 등 합병 관련 주요 정보를 시장에 투명하게 공시하도록 하는 것이 필요하다. 이러한 공시를 검토한 결과 주주의 이익을 해할 수 있는 합병으로 판단될 경우 주주들이 합병에 대한 문제를 제기할 수 있도록 절차적으로 보호하는 제도의 보완이 필요하고, 계열사간의 합병에서는 그러한 공정성을 위한 절차를 더욱 강화해야 한다.27)
금융당국이 발표한 제도개선방안에 따르면 비계열사간 합병만 자율화하고 계열사간 합병은 현행 제도를 유지하는 것으로 하고 있으나, 앞서 언급한 문제점에 비추어 볼 때 계열사간 합병 역시 자율화하되 공정성을 담보하기 위한 다른 방안으로 보완하는 것이 적절하다. 계열사간 합병에 대주주의 영향력에 대한 우려가 있다 하여도 합병가액의 평가를 시가에 의존하는 것이 오히려 시가의 왜곡을 불러올 수 있는 한계도 존재하고28), 합병가액의 산정방식을 자율화하고 그 타당성을 회사가 입증하게 한다면 시장에서 이에 대한 판단을 할 수 있게 마련이다. 만약 합병비율이 일반주주에게 불리하게 제안될 경우, 기관투자자가 적극적으로 반대 의사를 표시하고 다수의 소수주주가 주식매수청구권을 행사할 경우 합병비율의 조정이 이루어질 수 있게 된다. 이러한 점에 비추어 볼 때 계열사간 합병을 자율화 한다고 하여 일반 주주에 불리한 합병비율이 제시될 것이라고 사전에 예단할 수 없을 것이다.
2. 합병가액 산정방식에 대한 공시 강화
합병하는 회사의 이사회에서 합병가액을 자유롭게 산정하고, 그 산정방식과 가격의 적정성에 대한 구체적 정보를 공시하도록 하여, 주주들과 시장 참여자들이 합병에 대해 판단할 수 있도록 하여야 한다.29) 현재도 회사가 합병계약을 체결하면 이사회 또는 합병계약서 체결 후 3일 이내에 주요사항보고서를 제출하여 공시하도록 하고 있다. 이 때 이사회의사록, 합병계약서, 외부평가의견서 등의 서류를 첨부하여야 하고, 기업공시서식에 의해 합병의 목적, 합병의 중요 영향 및 효과, 합병비율, 합병비율의 산출근거가 공시되고는 있다. 그러나 현재 공시되는 내용만으로는 투자자 입장에서 합병비율의 적정성과 합병의 타당성 등을 검토하기에 충분하지 않다.
미국의 경우 SEC는 합병과 관련하여 다양한 보고서를 요구하는데30), 특히 주주총회 이전에 주주들의 합병 찬반의 의사결정을 돕기 위해 제공되는 보고서인 DEFM 14A 양식에는 합병과 관련하여 상세한 정보를 제공하도록 하고 있다. 구체적으로 합병의 배경, 경과와 합병가액 적정성을 포함한 합병의 긍정적·부정적 요인 관련 이사회 의견, 합병에 대한 임원의 이해관계, 합병 자금 조달, 외부 전문가의 의견 등이 포함되어 있다. 합병 관련 또 다른 공시서식인 S-4에서는 거래 조건, 위험 요소, 비율, 추정 재무 정보 및 인수 대상 회사와의 중요한 계약에 관한 정보를 포함할 것을 요구한다. 영국의 경우 합병의 효과, 중요한 이해관계에 미치는 영향, 합병의 내용, 합병비율의 법률적/경제적 측면의 검토내용과 결과 등이 포함된 이사회 설명보고서를 작성하여야 하고(회사법 제908조), 독립된 외부 전문가의 의견31)도 함께 공시하여야 한다(회사법 제909조). 독일 역시 합병보고서에 합병목적, 합병비율과 합병교부금, 합병계약서에 대한 법적·경제적 설명과 근거를 요구하며 특히 합병하는 회사의 기업가치 평가 시 특별한 어려움과 합병이 주주의 지분관계에 미치는 영향에 대한 설명이 담기도록 하고 있다(조직재편법 제8조). 일본의 경우 법에서 합병대가의 산정방법과 그 상당성에 관한 사항뿐 아니라 계열회사간 합병의 경우 소멸회사의 주주의 이익을 해치지 않도록 유의한 조치에 대한 내용32)을 기재하도록 하고 있다(회사법 제782조). 더불어 금융상품거래법에 따른 주요사항신고서와 유가증권신고서에 합병비율, 산정방법, 외부기관자문여부 및 그 내용을 기재하는데 특히 존속회사/소멸회사별로 타당성 확보 및 이해상충방지를 위한 조치내용을 포함하여 기재하도록 하고 있다.
이러한 해외 입법례를 참고하여 상법 또는 자본시장법의 상장법인 특례규정을 개정하거나 공시서식을 개정하여 더 많은 정보가 투자자들에게 제공되도록 하고, 합병의 타당성과 공정성에 대해 회사가 투자자들에게 적극적으로 설명하도록 하는 것이 필요하다. 특히 합병비율의 구체적 산정근거와 적정성에 대한 이사회의 의견이 반드시 포함되도록 하고 계열사간 합병의 경우 합병이 지분관계 등 중요한 이해관계에 미치는 영향을 공시하도록 하며, 주주들의 이익을 보호하기 위한 조치(독립적 외부평가, 독립위원회의 심의를 통한 합병가액 결정) 등 회사가 취한 공정성 담보방안을 함께 공시하도록 하는 방안도 고려하여야 한다.
3. 주주의 이익을 해할 우려가 있는 합병의 공정성 담보 방안
합병가액 산정방식 등에 대한 내용이 구체적으로 사전에 공시된 경우, 주주들이 이를 확인하고 불이익을 입을 우려가 있으면 문제제기할 수 있는 추가적인 방안을 마련할 필요가 있다. 이를 위해 해외 주요국의 입법례에서 인정하고 있는 합병유지청구권, 합병검사인제도, 합병관계자의 손해배상책임을 도입할 것을 제안한다. 다만 모든 합병에 이를 적용하는 것이 아니라, 주주의 이익을 해할 우려가 있을 경우 주주의 요청에 의해 행사할 수 있도록 제도를 설계하도록 하는 것이 필요하다. 특히 1명의 주주가 요청할 경우 허용되는 단독주주권이 아니라 일정 지분율 이상의 주주가 요구할 때 인정되는 소수주주권으로 도입하여야 한다. 사실상 합병의 불공정에 대한 문제가 제기되는 사례는 적은데, 이를 모든 합병에 요구한다면 도리어 합병이 저해되고 일부 주주의 문제제기로 대다수 주주가 피해를 입는 부작용이 우려되기 때문이다.
가. 합병유지청구권 도입
합병가액 산정방식이 사전에 공시된 경우, 주주들이 이를 확인하고 불이익을 입을 우려가 있으면 유지청구권을 행사할 수 있도록 합병유지청구권을 도입하는 것이 필요하다.33) 현행 상법에서는 이사가 법령 또는 정관에 위반한 행위를 하여 이로 인하여 회사에 회복할 수 없는 손해가 생길 염려가 있는 경우에만 유지청구권을 허용하는데(제402조), 합병에서 회사의 손해와 주주의 손해는 다를 수 있어 주주가 유지청구권을 행사하는데 한계가 있다. 이에 일본에서는 회사법을 개정하여, 합병 등의 조직재편시 주주들이 사전적으로 유지청구권을 행사할 수 있도록 규정하였다(제796조의2). 주주가 불이익을 받을 염려가 있을 때에는 주주는 회사에 대해 합병을 중지할 것을 청구할 수 있다. 미국의 경우에도 주주가 유지명령청구권을 행사할 수 있다.34) 해당 합병거래가 사기적이거나35) 주식의 저평가와 관련하여 반대 소수주주에게 명백하게 해를 주는 재량권의 남용, 신뢰위반, 임무해태와 같은 문제가 있는 경우36)에도 유지명령청구가 허용된다.
나. 합병검사인제도
현행 상법에서는 총회검사인37)이나 현물출자검사인38)제도를 두고 있는데, 소수주주권으로 합병검사인제도를 도입하는 것을 검토할 수 있다.39) 합병가액의 산정은 회사들이 자율적으로 정하도록 하되, 회사가 정한 합병비율과 판단근거가 적정한지를 객관적이고 전문성 있는 제3자가 검토하도록 한다면 합병가액 및 절차의 공정성을 담보하는데 기여할 수 있을 것이다.40) 독일의 경우 완전모자회사간 합병이 아닌 이상, 합병계약에 합병검사인의 선임을 의무화하고 있다(조직재편법 제9조 및 제10조). 합병검사인은 대표이사의 신청에 따라 법원에 의하여 선출되고 임명되며, 합병비율의 산정방법 및 그 적정성, 복수의 평가방법이 사용되었다면 평가방법별로 어떠한 합병비율이 산정되었고 어떤 가중치를 부여하였는지 등을 평가하고 서면으로 보고서를 작성하여 주주총회 전에 제출한다(조직재편법 제12조). 다만 주주총회 전까지 신속한 검토를 위해, 합병검사인이 직접 합병회사를 평가하는 것이 아니라 회사가 사전에 제출한 자료를 토대로 적정성을 평가한다. 이러한 합병검사보고서는 합병비율의 공정성을 담보하는 수단으로 실무에서 상당히 성공적인 것으로 평가받고 있다.41)
다. 합병 관계자의 손해배상책임 인정
우리 상법에서는 이사의 손해배상책임을 인정하지만, 유지청구권과 마찬가지로 회사에 손해가 발생한 경우에만 책임을 지게 된다(제399조).42) 그런데 합병과 같은 조직재편에서 회사의 손해와 주주의 손해는 다를 수 있고 특히 지배주주와 소수주주간 이해상충으로 소수주주에게만 손해가 발생한 경우에는 이사에 대해 책임을 추궁하기 어렵다. 이러한 문제를 인식하고 독일에서는 소멸회사의 경영진에게 합병비율을 결정할 때 주주가 손해를 입지 않도록 주의를 기울이도록 하고, 주의의무를 소홀히 하여 소멸회사의 주주가 손해를 입으면 주주는 이사를 상대로 직접 손해배상을 청구할 수 있도록 하고 있다(조직재편법 제25조).43) 합병과 같은 조직재편에서 이러한 손해배상책임을 도입하는 것도 소수주주를 보호하고 합병의 공정성을 담보할 수 있는 대안이 될 수 있다. 외부평가기관의 선임과정에서 위법이 있을 경우 선임기관에 대한 손해배상책임을 인정하고, 외부평가기관의 평가와 관련하여 외감법 제31조44)나 자본시장법 제125조45)와 같은 손해배상책임을 규정하도록 한다. 독일식 합병검사인제도가 도입된다면, 합병검사인의 손해배상책임 규정도 함께 마련하여야 한다.
Ⅳ. 나가며
시장주가를 기준으로 산정하는 합병가액 산정방식이 관행으로 자리잡았으나, 시장주가에 의존한 합병가액 산정방식과 합병시점의 임의성, 합병가액의 불확실성 등의 문제로 인해 당초 입법목적과 달리 투자자 보호에 기여하지 못하고 있는 현실이다. 또한 합병가액에 대한 규제가 도입될 당시와 MSCI 선진국지수의 편입을 도전하는 현재의 자본시장이 다르다는 점에 비추어 볼 때도 제도 개선의 필요성이 요구된다. 1990년대는 자본시장의 규모가 작았고 자본시장의 인프라도 발달하지 않아서 감독당국이 후견적 역할을 하였으나, 이제는 합병가액의 적절성과 공정성에 대해 회사가 제공한 정보를 토대로 하여 시장에서 이해관계자들이 평가할 수 있도록 하는 것이 적절하다.
합병가액을 자율화하되, 계열사간 합병과 비계열사간 합병을 나누지 않는 방향으로 추진해야 한다. 기업가치를 토대로 하는 합병가액의 산정방식은 동일하게 하되, 이해관계자간 거래의 경우 합병가액 산정과 합병절차의 공정성을 강화하는 방안으로 추진하는 것이 바람직하다. 지금까지는 법에서 합병가액 산정방식을 정하고 있었으니 회사 입장에서 그 적정성이나 타당성을 적극적으로 주장하지 않았으나, 이를 자율화할 경우 계열사간 합병에서 회사는 공정성을 더 입증하려 할 것이다. 계열사간 합병의 경우 시장은 대주주의 영향력에 대해 관심을 가지고 볼 것이기 때문에, 주주총회에서 주주들의 찬성을 얻기 위해 그리고 유지청구권이나 합병검사인 등의 소수주주권 행사를 피하기 위해 회사는 더 적극적으로 합병가액의 적정성과 타당성을 입증하려 할 것이다. 이러한 합병가액의 자율화 및 공시강화, 주주의 이익을 해할 우려가 있는 합병의 공정성 담보를 위한 제도 개선이 실질적인 투자자 보호와 자본시장에 대한 신뢰도 향상에 기여할 것으로 기대한다.
1) 금융위원회(2023. 5. 8)
2) 독일의 경우 증권취득 및 인수에 관한 법률에 의해 공개매수시 인수자의 제안 직전 3개월 이내의 거래량 가중평균주가 및 최근 6개월간 있었던 다른 제안가격 중 가장 높은 가격으로 정하도록 규제하나, 이는 합병하는 회사가 자율적 협의로 정하는 합병가액과는 다르다.
3) 합병에는 흡수합병과 신설합병이 있으나, 우리나라의 경우 신설합병이 매우 드물고 흡수합병이 대부분이기에 흡수합병을 기준으로 합병의 정의를 설명하였다.
4) 합병에 반대하는 주주에게 주식매수청구권이 인정되나, 이는 회사에 남지 않겠다는 주주들의 주식을 회사가 매수해 주는 제도일 뿐 회사에 계속 머물면서 정당한 주식가치를 보장받기 원하는 주주들을 보호할 수 있는 제도는 아니다.
5) 2009년 증권거래법이 폐지되면서 합병 관련 규정이 자본시장법으로 이관되었다.
6) 가중평균 계산 시 가중치는 거래량으로 한다.
7) 김건식(2015, p.86), 송옥렬(2023, p.1244)
8) 김희준(2015, p.352)
9) 김홍기(2011, pp.181-182)
10) 권기범(2011, p.155)
11) 주권상장법인은 공개시장에서 다수 투자자들의 자유로운 거래에 의하여 그 주가가 형성되는 것이어서 공개시장에서 형성된 주가가 해당 상장법인의 일정시점에 있어서의 가치를 비교적 객관적으로 반영한다고 볼 여지가 있는 점 등을 고려하여 합병에 있어 핵심적인 요소인 합병가액을 미리 법령에서 마련한 일정한 방식에 의하도록 하면서 그 구체적 사정에 있어서는 비교적 객관적 기준이라 볼 여지가 있는 공개시장의 주가를 기준으로 삼도록 한 것이다(서울고등법원 2015. 7. 16 자 2015라20485 결정).
12) 미국과 일본의 실제 거래액을 비교할 때는 ‘합병가액’이 아니라 ‘합병액’이라는 용어를 사용하고자 한다. ‘합병가액’은 1주당 가격인 반면, ‘합병액’은 발행주식총수를 곱한 전체 거래액으로, 전체 합병규모를 정확하게 비교하기 위해 ‘합병액’이라는 용어로 사용한다. 즉 본 보고서에서 사용한 합병액은 합병가액 × 발행주식총수이다.
13) 블룸버그 데이터를 이용하여 분석을 시행했는데, 블룸버그에서는 기업의 인수합병이 발생한 경우, 존속회사와 소멸회사의 이름, 인수합병이 발표된 날짜, 성사된 인수합병의 가치(Announced total value), 소멸회사의 TV/EBITA 등의 정보를 제공한다. 이 중 2019년 1월에서 2023년 4월까지 상장법인간 인수합병이 발표된 데이터를 추출하였다. 블룸버그에서는 해당 거래가 합병(merger)인지 인수(acquisition)인지는 구분하지 않고 있어, 인수합병이 발생한 이후 150일 거래일 내에 소멸회사가 상장폐지된 경우를 합병으로 간주해 분석에 이용하였다. 분석의 편의를 위하여 존속회사와 소멸회사가 모두 미국기업인 경우로 제한하였다.
14) 기업의 시장가격과 실제 합병액과 자본시장법에 따른 합병액의 차이의 절대값을 기업의 시장가격으로 나눈 값은 약한 음의 상관관계(-0.0542)를 보이나, 통계적으로 유의한 수준은 아니다.
15) 일본의 경우 존속회사가 합병 이전에 이미 소멸회사의 주식을 취득하고 있는 경우가 존재하였고(계열사간 합병 포함), 해당 경우 블룸버그에는 추가로 취득하는 주식의 가격이 거래가격으로 기록하였다. 자본시장법상의 합병가액과의 적절한 비교를 위하여, 블룸버그에 공개된 거래 가격 대신, EDINET에 공시된 주식매수청구권의 가격 및 언론 보도자료를 참고한 소멸회사 거래가격을 분석에 이용하였다. 분석에 사용된 합병은 존속회사와 소멸회사가 모두 일본기업인 경우로 제한하였다.
16) 기업의 시장가격과 실제 합병액과 자본시장법에 따른 합병액 차이의 절대값을 기업의 시장가격으로 나눈 값은 약한 음의 상관관계(-0.0359)를 보이나, 통계적으로 유의한 수준은 아니다.
17) 손창완(2019, p.284)
18) 자본시장법은 계열사간 합병의 경우 기준시가의 10% 내, 비계열사간 합병의 경우 30% 내에서 합병가액의 할인 또는 할증이 가능하다고 규정하고 있으나, 할증 혹은 할인이 적용된 사례는 전무하였다. 따라서 합병가액에 대해 외부평가기관의 평가를 받는 경우도 나타나지 않았다.
19) 2018년부터 2022년까지 상장법인간 합병 중, 합병 발표 시점 1년전 시장에 상장된 29개 기업의 합병 발표 1년 전부터 합병 발표일까지 1년 누적 시장조정수익률의 평균값이다.
20) 권기범(2011, pp.171-173)
21) 대법원 2010. 7. 22. 선고 2008다37193 판결(이랜드·이랜드월드 분할합병 사건), 대법원 2009. 4. 23. 선고 2005다22701,22718 판결(국민은행·한국주택은행 합병 사건), 대법원 2008. 1. 10. 선고 2007다64136 판결(남한제지·풍만제지 합병 사건)
22) 삼성물산과 제일모직의 합병에 대한 합병무효의 소는 서울고등법원에서 2심 중에 당사자가 항소를 취하하였다(2022. 5.).
23) 김지환(2017, p.335), 최민용(2017, p.146)
24) 노혁준(2016, p.97)
25) 노혁준(2016, p.88)
26) 김건식(2015, p.87)
27) 미국의 경우에도 계열사간 합병에서는 강화된 공정성을 요구하고 있는데, 2014년 델라웨어 주에서는 Kahn v. M&F Worldwide Corp. 판결에서 특별이해관계자와의 합병에서 사외이사로 구성된 독립적인 특별위원회와 소수주주의 과반수가 모두 승인한다면 공정성이 추정되어 경영판단원칙이 적용된다고 판시하였다.
28) 노혁준(2016, p.131)
29) 정형찬(2019, p.189)
30) SEC는 주요사항보고서(8-k)로 합병에 대한 결정을 공시하도록 하고 있고, 합병결정 공시이후 SEC에 합병 위임장을 제출하도록 한다(DEFM14A). 합병 위임장은 합병에 대한 주주총회 이전에 합병계약 관련 구체적 정보를 주주들에게 제공하는 서류인데, 예비위임장(PREM14A)을 먼저 제출하고 최종 위임장(DEFM14A)을 제출하기도 한다. 합병 또는 교환 제안의 일부로 신주가 발행되는 경우 취득자는 취득자의 주주가 주식 발행을 승인하도록 요청하는 등록 명세서(S-4)를 제출하도록 한다.
31) 합병비율을 산출하는데 사용한 방법 또는 복수의 방법을 표시하고 해당 방법이 합리적인지에 대한 의 견과 합병비율이 합리적인지 여부를 기재하여야 한다. 이를 위해 합병회사의 모든 해당 서류에 대한 접근권과 회사 임원에 대하여 합병 관련 정보의 요구권을 갖는다(회사법 제909조).
32) 각 회사의 기업가치 산정에서 독립된 제3자의 외부평가를 받은 내용, 이해관계자를 가진 이사를 합병결의에서 제외한 것, 사외이사 또는 독립위원회에서 심의하여 합병대가를 결정한 것 등의 주주 보호 조치에 대해 회사가 설명하도록 하고 있다.
33) 김지환(2017, p.337)
34) 황현영(2012, p.38)
35) Young v. ValhiInc., 382 A 2d 1372 (Del. Ch. 1978)
36) In Cole v. National Gas Credit Corp., 156A. 2d 187-188 (Del. Ch. 1931)
37) 상법 제367조(검사인의 선임) ① 총회는 이사가 제출한 서류와 감사의 보고서를 조사하게 하기 위하여 검사인(檢査人)을 선임할 수 있다. ② 회사 또는 발행주식총수의 100분의 1 이상에 해당하는 주식을 가진 주주는 총회의 소집절차나 결의방법의 적법성을 조사하기 위하여 총회 전에 법원에 검사인의 선임을 청구할 수 있다.
38) 상법 제299조(검사인의 조사, 보고) ① 검사인은 제290조 각 호의 사항과 제295조에 따른 현물출자의 이행을 조사하여 법원에 보고하여야 한다.
39) 노혁준(2016, p.107)
40) 합병절차의 공정성 담보를 위해 소수주주의 다수결을 도입하자는 의견도 있으나, 이는 미국에서 회사가 자신들이 추진하는 합병의 공정함을 입증하기 위해 자발적으로 채택한 방안 중 하나로 법에서 이를 강제하는 것은 적절하지 않다고 본다. 즉 회사가 자발적으로 소수주주의 다수결 절차를 거쳤다면 합병이 공정하다고 볼 수 있는 근거가 될 뿐이다.
41) 정대익(2018, p.322)
42) 상법 제401조에 의해 주주의 직접손해에 대한 이사의 손해배상책임도 인정이 되지만, 합병과 같은 조직재편에서 주주의 손해는 직접손해가 아닌 간접손해이기 때문에 보호받지 못한다.
43) 다만 독일의 경우 존속회사의 주주들은 존속회사의 이사를 상대로 손해배상책임을 추궁할 수 없고, 소멸회사의 주주들만 가능하다.
44) 외감법 제31조(손해배상책임) ① 감사인이 그 임무를 게을리하여 회사에 손해를 발생하게 한 경우에는 그 감사인은 회사에 손해를 배상할 책임이 있다. ② 감사인이 중요한 사항에 관하여 감사보고서에 적지 아니하거나 거짓으로 적음으로써 이를 믿고 이용한 제3자에게 손해를 발생하게 한 경우에는 그 감사인은 제3자에게 손해를 배상할 책임이 있다. 다만, 연결재무제표에 대한 감사보고서에 중요한 사항을 적지 아니하거나 거짓으로 적은 책임이 종속회사 또는 관계회사의 감사인에게 있는 경우에는 해당 감사인은 이를 믿고 이용한 제3자에게 손해를 배상할 책임이 있다.
45) 자본시장법 제125조(거짓의 기재 등으로 인한 배상책임) ① 증권신고서(정정신고서 및 첨부서류를 포함한다. 이하 이 조에서 같다)와 투자설명서(예비투자설명서 및 간이투자설명서를 포함한다. 이하 이 조에서 같다) 중 중요사항에 관하여 거짓의 기재 또는 표시가 있거나 중요사항이 기재 또는 표시되지 아니함으로써 증권의 취득자가 손해를 입은 경우에는 다음 각 호의 자는 그 손해에 관하여 배상의 책임을 진다. 다만, 배상의 책임을 질 자가 상당한 주의를 하였음에도 불구하고 이를 알 수 없었음을 증명하거나 그 증권의 취득자가 취득의 청약을 할 때에 그 사실을 안 경우에는 배상의 책임을 지지 아니한다.
참고문헌
고봉찬ㆍ김진우, 2023, 기업가치 평가 관련 규정과 현금흐름할인법의 도입 필요성, 『한국 증권학회지』52(2), 301-329.
권기범, 2011, 『기업구조조정법(제4판)』, 삼영사.
권재열, 2015, 삼성물산 대 엘리엇 결정 – 주요쟁점의 재검토, 『상사판례연구』 28(4), 3-54.
금융감독원, 2009. 6. 23, 자산평가의 공정성 확보를 위한 「외부평가업무가이드라인」 제정, 보도자료.
금융위원회, 2023. 5. 8, 기업 M&A 지원방안, 보도자료.
김건식, 2015, 삼성물산 합병사례를 통해 본 우리 기업지배구조의 과제, 『BFL』 74, 83-101.
김배정, 2015, 합병비율의 공정성을 위한 제언, 『법학연구』 56(4), 163-192.
김지환, 2017, 주식매수청구권에 대한 재검토, 『상사법연구』 36(2), 307-346.
김홍기, 2011, 현행 주식가치평가의 법적 쟁점과 ‘공정한 가액’에 관한 연구, 『상사법연구』 30(1), 159-205.
김희준, 2015, 상장법인 간 합병에 적용되는 합병비율 산정방식 검토 - 삼성물산과 제일모직의 합병사례를 중심으로, 『상사법연구』 34(3), 331-366.
노혁준, 2016, 합병비율의 불공정성과 소수주주 보호 – 유기적 제도설계를 향하여 –, 『경영법률』 26(2), 87-138.
손창완, 2019, 상장회사 합병과 합병비율의 공정성 – 관련 규정 및 사례에 대한 비판적 검토, 『상사법연구』 38(3), 235-296.
송옥렬, 2023, 『상법강의(제13판)』, 홍문사.
임재연, 2008, 『증권거래법(전정판)』, 박영사.
정대익, 2018, 합병비율 불공정에 대한 독일의 사후적 구제수단, 『금융법연구』 15(3), 317-365.
정형찬, 2019, 합병비율 산정에 관한 자본시장법 시행령의 개정 방향, 『경영법률』 29(4), 155-200.
최민용, 2017, 계열사 간의 합병과 회사법적 규제, 『상사판례연구』 30(3), 115-161.
최성근, 2019, 상법과 자본시장법의 주식평가방법에 대한 해석론 및 입법론, 『상사법연구』 38(1), 179-220.
최순영ㆍ김종민, 2018, 『기업 소유구조가 국내 상장사 간 합병에 미치는 영향 분석』, 자본시장연구원 연구보고서, 18-02.
황현영, 2012, 상법상 강제매수제도에 관한 연구, 한양대학교 대학원 박사학위 논문.
황현영, 2013, 회사의 조직재편시 공정한 주식가치평가에 대한 제언, 『법과 정책연구』 13(1), 65-87.

